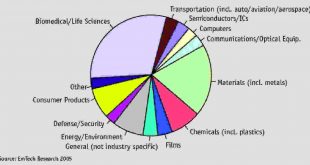
Nanotechnology deals with the understanding, control, and manufacture of matter in the nanoscale regime, usually between 1 nm to 100 nm, and exploiting them for a useful application. At this length scale, unique properties and phenomena arise as a result of increased surface-to-volume ratio and dominance of quantum mechanical effects. …
Read More »Perovskite quantum dots attractive for LED displays, quantum dot solar cells and single photon emitter
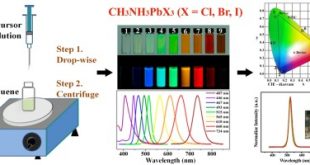
In the past few years, metal halide perovskite quantum dots and nanocrystals have been extensively explored due to their unique optoelectronic properties and extensive application prospects. Perovskites are materials that share a crystal structure similar to the mineral called perovskite, which consists of calcium titanium oxide (CaTiO3). Depending on which …
Read More »Metamaterials for Sensitive Biomolecule Sensing and Imaging
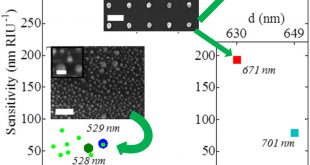
The ability to design and fabricate materials with new functionalities opens the door to a new world of possibilities. They can be tailored to either augment the functionality of existing devices or create new devices with superior performances. Metamaterials are artificially structured materials designed to control and manipulate physical phenomena …
Read More »Ultra-compact Nano antennas made of Nano Materials have applications from wearables to airplanes, spacecraft and military
An antenna is a device used to propagate, receive, and/or transmit electromagnetic waves which can have information embedded within them. The antenna creates an electromagnetic wave that carries the original embedded sound information through the atmosphere/space around it. An antenna at a different location, receives the electromagnetic wave, sending it …
Read More »Twisted light technology
Space-division multiplexing (SDM) has recently attracted great attention as a promising technology to further improve the transmission capacity and spectral efficiency. Very recently, SDM employing twisted lights, also known as orbital angular momentum (OAM) carrying lights, provides an alternative approach to increasing the transmission capacity and spectral efficiency of optical communications. …
Read More »Nanotechnology enhanced weapons and Nanoweapons are growing Global Security Threat with potential to cause human extinction
Nanotechnologies involve designing and producing objects or structures at a very small scale, on the level of 100 nanometres (100 millionth of a millimetre) or less. It allows humans to play with the building blocks of the universe, exploiting the laws of quantum mechanics to construct materials with unimaginable precision – …
Read More »Nanotechnology enhanced Supercapacitors, including Graphene and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) provide superfast battery charging in electric vehicles to wearable electronics
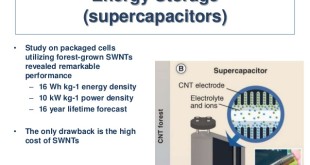
The rapid increase in global energy consumption and the environmental impact of traditional energy resources pose serious challenges to human health, energy security, and the environment; and reveal a growing need to develop new types of clean and sustainable energy solutions such as electric vehicles with low exhaust emissions. However the …
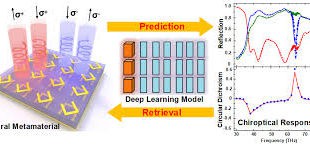
Read More »Machine learning enable designing new Metamaterials with desired property in days
Metamaterials are artificially structured materials designed to control and manipulate physical phenomena such as light and other electromagnetic waves, sound waves and seismic waves in unconventional ways, resulting in exotic behavior that’s not found in nature. They are predicted to be able to protect the building from earthquakes by bending …
Read More »Boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) considered the strongest light-weight nanomaterial.
Nanomaterials (NMs) have gained prominence in technological advancements due to their tunable physical, chemical and biological properties with enhanced performance over their bulk counterparts. NMs are categorized depending on their size, composition, shape, and origin. Newly discovered materials such as fullerene, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), graphene, transition metal dichalcogenides, hexagonal boron nitride …
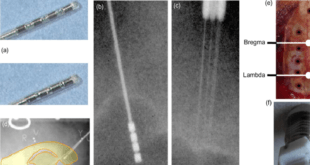
Read More »Electrode Materials are key to Brain Computer Interface (BCI) technology
Every action our body performs begins with a thought, and with every thought comes an electrical signal. The electrical signals can be received by the brain-computer interface, consisting of an electroencephalograph (EEG) or an implanted electrode, which can then be translated, and then sent to the performing hardware to produce …
Read More » International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis