Modern microelectronic semiconductors and integrated circuits provide remarkable computational and memory capabilities but lack the capability to interface with the physical world directly. MEMS (MicroElectroMechanical Systems) and the even smaller NEMS (Nano ElectroMechanical Systems) integrate sensors and actuators on microelectronic circuitry and enabling these products, awareness of the surroundings in …
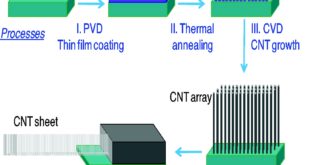
Read More »Carbon Nanotubes assembly, manufacturing integration processes usher carbon revolution for post silicon future
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are hollow cylindrical tubes formed by rolling a sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal ring, as in a sheet of graphite, either in monolayer (single-walled nanotube, SWCNT) or multilayer (multi-walled nanotube, MWCNT) form. CNTs exhibit different electronic properties based on the way these graphene …
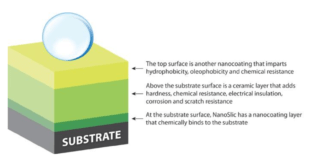
Read More »Nanocoatings for consumer and military electronic devices
Nanotechnology is an industry that has recently begun to offer breakthrough solutions to the world. The incorporation of nanomaterials into thin films, coatings and surfaces leads to new functionalities, completely innovative characteristics and the possibility to achieve multi-functional coatings and smart coatings. The use of nanomaterials also results in performance enhancements …
Read More »Nanocoatings provide multiple functionalities in the aerospace, defense, medical, and marine applications
Nanotechnology is an industry that has recently begun to offer breakthrough solutions to the world. The incorporation of nanomaterials into thin films, coatings and surfaces leads to new functionalities, completely innovative characteristics and the possibility to achieve multi-functional coatings and smart coatings. The use of nanomaterials also results in performance enhancements …
Read More »Emerging Quantum metamaterials and metasurfaces are an entirely new type of materials enabling quantum computers and sensors
Metamaterials are artificial materials designed to control the electromagnetic properties of a medium. Metasurfaces are the two-dimensional version of metamaterials: extremely thin surfaces made up of numerous subwavelength optical nanoantennas, each designed to serve a specific function upon the interaction with light. The metasurfaces contain regularly spaced nanoparticles that can …
Read More »Global advanced functional and multifunctional materials market
Smart materials or Active materials or Functional materials are designed materials that have diverse, dynamic features that enable them to adapt to the environment. They have one or more properties that can be significantly changed in a controlled fashion by external stimuli, the stimulus and response may be mechanical, electrical, …
Read More »Graphene for implementing scalable quantum computer
Quantum computing is expected to increase significantly the computational speed since it operates on completely different principles in comparison to classical computers. In addition, it was predicted that quantum computers can increase the computational speed of at least some problems. For instance, a sub-exponential speed-up is expected if the quantum …
Read More »Single layer (monolayer) of a semiconducting material technologies
With a view to future applications in electronics and quantum technology, researchers are focusing on the development of new components that consist of a single layer (monolayer) of a semiconducting material. Some naturally occurring materials with semiconducting properties feature monolayers of this kind, stacked to form a three-dimensional crystal. In …
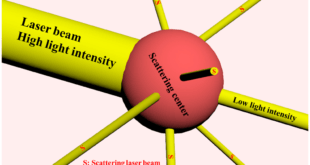
Read More »Nanomaterials for protection from laser weapons
Laser attacks targeting pilots and air crews are a major concern across the world with most attacks reported to take place during take-off and landing. According to figures from the US Federal Aviation Authority, there were 6,753 laser illuminations reported in 2017. Until recently, the expense of lasers had limited their use …
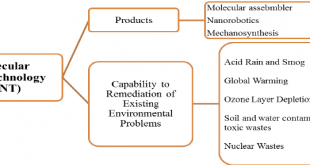
Read More »Molecular nanotechnology
The amount of information trafficking internet nowadays is enormous and will increase further in the near future. It can be expected that in the next decennia the current technologies to store and process data will no longer suffice and that other strategies to handle information have to be developed. One …
Read More » International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis