Laser technology provides major advantages for military applications over kinetic weapons due to High precision and rapid on-target effect, precise and scalable effects, avoidance of collateral damage caused by fragmenting ammunition, Low logistics overhead, and minimum costs per firing. The proliferation of small, low-cost Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) on …
Read More »Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) sensors
The fiber optic sensors also called as optical fiber sensors use optical fiber or sensing element. These Sensors can measure a large variety of parameters, such as temperature, pressure, strain, refractive index, vibrations, displacements, bending, loading, and liquid level or concentration of chemical species. Over the past decade, the …
Read More »Compound semiconductors for 5G, radar, electronic warfare, aviation, and satellite communication applications
Modern electronic products, from computers to smart phones, use silicon chips at their heart. As the name suggests, these chips are made from silicon, which is a highly abundant element found in sand. With a single element, it is possible to scale-up the manufacturing process to make highly complex silicon chips …
Read More »Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) Accelerometer
Over the past decade, the proliferation of fiber optic sensors and sensing systems has been ever-increasing, especially the use of fiber Bragg grating (FBG) based sensors. The fiber optic sensors also called as optical fiber sensors use optical fiber or sensing element. These Sensors can measure a large variety of parameters, …
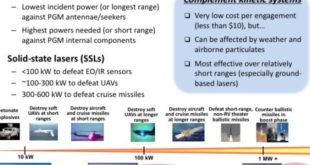
Read More »Petawatt laser technologies for Ballistic and Cruise to Hypersonic weapons defense
The Laser Directed Energy Weapons (DEWs) offer a transformational ‘ga me changer’ to counter asymmetric and disruptive threats, while facing increasingly sophisticated traditional challenges. Laser technology provides major advantages for military applications over kinetic weapons due to High precision and rapid on-target effect, precise and scalable effects, avoidance of collateral …
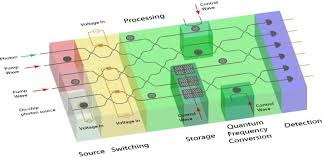
Read More »Photonic Integrated Circuits technologies promise Quantum computers and sensors, as system-on-chip solutions integrated into laptops and cell phones.
Photonics is a breakthrough technology as it uses photons (smallest unit of light) as the data carrier instead of electrons (smallest unit of electricity) used in electronic ICs. As light travels very high speeds, photonics is widely used to transfer huge amounts of data at a very high speed. Thus …
Read More »Reconfigurable Multi-GPU Systems enabled by Silicon Photonics
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized, electronic circuit designed to rapidly manipulate and alter memory to accelerate the creation of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display device. Modern GPUs are very efficient at manipulating computer graphics and image processing. GPUs were traditionally tasked …
Read More »Optical Fiber Network Technologies enabling terabit per second optical fiber networks for 5G, fiber-to-the-home (FTTH)
An optical network is a communication system that uses light signals, instead of electronic ones, to send information between two or more points. The points could be computers in an office, large urban centers or even nations in the global telecommunications system. These include limited range local-area networks (LAN) or wide-area …
Read More »DARPA P-IR developing very small, persistent infrared radiation (IR) sensors of personnel
Infrared radiation detectors are a critical component for DoD imaging systems used in areas such as military vehicles, military night vision, military communication, environmental monitoring, and target acquisition. In addition, they are crucial for commercial markets including surveillance, digital cameras, automotive and scientific research. Common constraints for IR sensors …
Read More »DARPA OpTIm developing room-temperature Quantum-Level Infrared Detectors
Electromagnetic energy, produced by the vibration of charged particles, travels in the form of waves through the atmosphere and the vacuum of space. These waves have different wavelengths (the distance from wave crest to wave crest) and frequencies, These two are inversely related to each other, the shorter the wavelength, …
Read More » International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis