A work-breakdown structure (WBS) in project management and systems engineering, is a deliverable-oriented breakdown of a project into smaller components. A work breakdown structure is a key project deliverable that organizes the team’s work into manageable sections phases, deliverables and work packages. The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK 5) defines the work-breakdown structure as a “hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables.”
In a project or contract, the WBS is developed by starting with the end objective and successively subdividing it into manageable components in terms of size, duration, and responsibility (e.g., systems, subsystems, components, tasks, subtasks, and work packages) which include all steps necessary to achieve the objective. A work-breakdown structure element may be a product, data, service, or any combination thereof. It is a tree structure, which shows a subdivision of effort required to achieve an objective; for example a program, project, and contract.
A WBS also provides the necessary framework for detailed cost estimating and control along with providing guidance for schedule development and control
NASA WBS Development Techniques
The following techniques can be helpful in the development of a project WBS:
a. Preparing functional requirement block diagrams
b. Coding WBS elements in a consistent manner
c. Preparing element tree diagrams
d. Preparing a WBS dictionary
e. Using development checklists
f. Using WBS templates
Preparing Functional Requirement Block Diagrams
A good place to begin developing a preliminary WBS is by listing the functional requirements for the new product or system. If the number of requirements is large, group them into similar categories. Create a parent or end product at the top of your list or graphic. Then, create subordinate major groupings of functional requirements with similar characteristics. Next, subdivide the major groupings into smaller groupingsthat have natural dividing points. Finally, translate this functional block diagram into a product structure.
In order to translate the functional block diagram into a product structure, begin at the top level with the desired end product that is completely integrated. At the first subordinate level, using the functional block diagram, create a major system block for each related functional block or blocks. The translation may result in a one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-one relationship between the functional blocks and the major system blocks. Create subsystem or other subordinate blocks that further define the major system blocks as necessary. Continue this process until the product structure is complete and all functional requirements are accounted for. The result is your initial WBS.
Coding WBS Elements in a Consistent Manner
Each WBS element is assigned a unique element code to be used as a reference point for its technical and financial identification throughout the life of the project. A simple decimal coding system that logically indicates the level of an element and related lower-level subordinate elements is applied.
Each NASA Project (Level 1) is assigned a six-digit numeric code such as 123456. Each sub-level code contains a two-digit numeric code separated from the previous level code by a period. Level 2 codes would appear as 123456.02 and Level 4 codes would look like 123456.02.07.05. A maximum of seven levels is allowed in the WBS coding structure contained in the Agency Core Financial System. The typical lowest level might appear as 123456.02.07.05.02.06.03 containing a maximum of 24 characters including all the periods.
Preparing Element Tree Diagrams
WBS tree diagrams are routinely developed to provide a visual display of a WBS. A pictorial view of the overall WBS aids all project staff in understanding how lower-level project components support and contribute to higher-level components. This type of diagram is often called a “family tree” or a “product tree” diagram.
Preparing a WBS Dictionary
A WBS dictionary lists and defines the WBS element contents. It is prepared by the project team for the purposes of ensuring that all work scope has been identified and to eliminate duplication and overlap of work assignments. Content ambiguities should be eliminated with clear statements describing the effort to be completed. The level of descriptive detail needed for each element should be commensurate with the element’s hierarchical position in the overall WBS structure. The lower the level of a WBS element, the greater the level of descriptive detail needed. The descriptive detail of element content should clearly identify all element interfaces.
Military & Aerospace
The WBS is a means of organizing system development activities based on system and product decompositions. It is a product-oriented family tree composed of hardware, software, services, data, and facilities, which result from systems engineering efforts during the development and production of the system and its components, and which completely defines the program. The WBS is prepared from both the physical and system architectures, and identifies all necessary products and services needed for the system. This top-down structure provides a continuity of flow down for all tasks. Enough levels must be provided to properly define work packages for cost and schedule control purposes
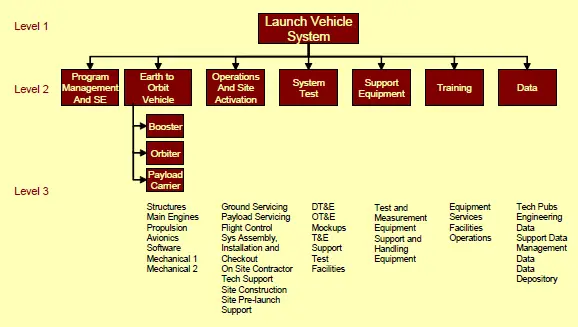
The Program Manager (PM) usually has the responsibility to develop an overall program WBS and to initiate development of contract WBSs for each contract in accordance with common DoD practice established in Mil-HDBK 881. The program WBS is the WBS that represents the total system and, therefore, describes the system architecture. The contract WBSs are part of the program WBS and relate to deliverables and tasks on a specific contract.
The PM with the support of systems engineering develops the first three levels of the program WBS, and to provide contractors with guidance for lower-level WBS development. As with most standards and handbooks, use of MIL-HDBK-881 cannot be specified as a contract requirement. Though WBS development is a systems engineering activity, it impacts costing, scheduling and budgeting professionals, as well as contracting officers. An integrated team representing these Stakeholders is needed to support WBS development.
The first three Work Breakdown Structure Levels are organized as:
Level 1: Overall System
Level 2: Major Elements (Segment)
Level 3: Subordinate Components (Prime Items)
Contractor Work Breakdown Statement
The contract WBS is the Government – approved WBS for program reporting purposes and includes all program elements (for example, hardware, software, services, data, or facilities), which are the contractor’s responsibility. It includes the contractor’s discretionary extension to lower levels, in accordance with Government direction and the contract Statement of Work (SOW).
 International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
