Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of technology, the convergence of various cutting-edge innovations is reshaping the way we perceive and utilize the cloud. Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Internet of Things (IoT), and the advent of 5G technology are revolutionizing the cloud computing landscape. This convergence has the potential to unleash unprecedented capabilities, paving the way for a smarter, more connected future. In this article, we will delve into how these technologies are coming together to revolutionize the cloud and explore the transformative implications they hold.
Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. It includes services such as networking, storage, analytics, and database.
You no longer have to manage and maintain your own hardware in your own data centers. Companies that provide cloud services enable users to store files and applications on remote servers and then access all the data via the Internet.
It enables businesses to lower their operational cost and facilitate faster scaling. That is why the market share of cloud computing is expanding at a rapid pace.
A cloud platform allows organizations to create cloud-native applications, test and build applications, and store, back up, and recover data. Cloud-native applications are software applications designed to be run in cloud computing environments, taking full advantage of cloud computing features and technologies such as scalability, resilience, and automation. They are developed using microservices architecture, which decomposes the application into small, independent services that can be developed, deployed, and managed separately. This allows for more efficient deployment and faster innovation, as well as greater resilience and scalability.
It also allows organizations to analyze data. Organizations can also stream video and audio, embed intelligence into their operations, and deliver software on-demand on a global scale.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a popular option for people and businesses for a number of reasons including cost savings, increased productivity, speed and efficiency, improved flexibility and scalability, performance, and security. It can also automate repetitive common tasks that don’t differentiate your business, like installing virtual machines or storing backups, enabling you to focus on what is strategically unique to your business. Another attractive point of the cloud is its ability to enable a mobile workforce, which brings enhanced flexibility and efficiency. Every day, millions of users are accessing online cloud services such as Apple iCloud, Gmail and Dropbox across desktop and mobile devices.
Pay as you go. Instead of investing in data centers and hardware before you know how you are going to use them, you pay only when you use computing resources, and pay only for how much you use.
Benefit from massive economies of scale. By using cloud computing, you can achieve a lower cost than you can get on your own. Because usage from hundreds of thousands of customers is aggregated in the cloud, AWS can achieve higher economies of scale, which translates into lower pay as-you-go prices.
Stop guessing capacity. Eliminate guessing on your infrastructure capacity needs. When you make a capacity decision prior to deploying an application, you often end up either sitting on expensive idle resources or dealing with limited capacity. With cloud computing, these problems go away. You can access as much or as little capacity as you need, and scale up and down as required with only a few minutes notice.
Increase speed and agility. IT resources are only a click away, which means that you reduce the time to make those resources available to your developers from weeks to just minutes. This results in a dramatic increase in agility for the organization since the cost and time it takes to experiment and develop is significantly lower.
Stop spending money running and maintaining data centers. Focus on projects that differentiate your business, not the infrastructure. Cloud computing lets you focus on your customers, rather than on the heavy lifting of racking, stacking, and powering physical infrastructure. This is often referred to as undifferentiated heavy lifting.
Go global in minutes. Easily deploy your application in multiple Regions around the world with just a few clicks. This means you can provide lower latency and a better experience for your customers at a minimal cost.
The major challenge of cloud service providers has been of ensuring security. Today, majority of organizations and many government departments and agencies have shifted their databases onto the cloud to improve efficiency and productivity of resources as well as bring down costs. Unfortunately, this move has exposed sensitive information to hackers, who have frequently launched cyber-attacks to retrieve and misuse data. For instance, the US-based Center for Strategic & International Studies (CSIS) revealed that in April 2020 hackers from Iran attempted to breach personal files of World Health Organization (WHO) staffers while the world was reeling under the coronavirus pandemic. In February 2020, two Chinese hackers were persecuted by the US Department of Justice for performing cryptocurrency laundering activities for North Korean nationals. Such attacks are prompted by the availability of delicate data on cloud platforms and the constant threat of privacy infringement may hinder the cloud computing market growth in the upcoming years.
But it seems soon all these asperations about safety are about to cast aside and cloud adoption rises in proportion to its benefits like mobility, greater than before efficiency, cost-effectiveness, simplified collaboration and high speed connectivity. With the massive exodus to the cloud, 80% of companies are predicted to close their traditional data centers by 2025, according to Gartner Research.
For more information on Cloud Computing please Visit
Types of Cloud Platforms
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has devised the following definition: “Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model promotes availability and is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models.”
The three main types of cloud computing consist of: private cloud, public cloud and hybrid cloud.
The services of the public cloud are provided over the Internet, off-site. In this model, third party cloud service providers offer end users the ability to access a range of services like email, social networking, marketing applications, data storage and more. All the resources used to deliver these services are owned and maintained by the third party service provider (e.g. Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform) and are shared by all users or subscribers to such public clouds. The public cloud offers the most in terms of shared resources and efficiency. The downside to this service is that they face more security and reliability issues than private clouds. Public cloud security is shared, therefore threats to security are also shared
Cloud services that are targeted towards just one company at a time, where all resources are used exclusively by one organization, typically come under the definition of private cloud. Infrastructure like servers and data centers may be located on premises or may be maintained in a remote location and managed by a third party vendor, just for a single company. Private clouds offer the highest level of control and security, but there is more cost involved than the public cloud. The business has to buy and maintain all the infrastructure and software, which increases the required investment.
Companies that want the best of both worlds, typically go down the route of building a hybrid cloud infrastructure. It allows access to both private and public cloud services for greater scalability and flexibility, with reduced resource overcapacity. The hybrid cloud lets you keep each part of your business in the most efficient environment. There is the drawback of having to keep track of several security platforms and be sure that all aspects of your company are able to communicate with one another.
Omni-cloud and Hybrid Cloud computing
The multicloud is the usage of more than one public or private cloud service with all cloud services residing either in public or private domains exclusively. Omni-cloud computing is a cloud solution that allows multiple cloud services to smoothly integrate and streamline their data on a single platform.
The omni-cloud system is being increasingly preferred over the multi-cloud system owing to its multiple advantages and leading the cloud computing market trends. For example, an omni-cloud tool makes possible accessing real-time information from any location. In a departmental store, for instance, whenever there is an inventory shortfall, the cloud will send notification to the authorities, who will then take the necessary action. Similarly, storage of data on a unified platform also enables efficient analysis, enhances productivity, and elevates the quality of services. These, along with a few other benefits, are widening the applicability of omni-cloud computing across a variety of industries.
There are also hybrid multicloud systems, like the Nutanix Enterprise Cloud, which help organizations manage all their various cloud ecosystems from a single, unified platform. Hybrid clouds allow companies to spread their apps, data and systems across a choice of private and public clouds, based on most critical requirement for each resource. For instance, mission-critical enterprise software may run on a private cloud, while applications like marketing automation tools that require lower security controls may be hived off on the public cloud. Research by Flexera reveals that 84% of enterprises have a multicloud strategy, with 58% reporting a hybrid approach to cloud computing.
Type of cloud services based on usage
Cloud computing is not a single piece of technology like a microchip or a cellphone. Rather, it’s a system primarily comprised of three services: software-as-a-service (SaaS), infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), and platform-as-a-service (PaaS). SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are simply three ways to describe how you can use the cloud for your business.
- PaaS: hardware and software tools available over the internet. Examples are AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku, Windows Azure (mostly used as PaaS), Force.com, OpenShift, Apache Stratos, Magento Commerce Cloud.
- IaaS: involves a method for delivering everything from operating systems to servers and storage through IP-based connectivity as part of an on-demand service. . Cloud-based services, pay-as-you-go for services such as storage, networking, and virtualization. Examples are AWS EC2, Rackspace, Google Compute Engine (GCE), Digital Ocean, Magento 1 Enterprise Edition
- SaaS: involves the licensure of a software application to customers. Licenses are typically provided through a pay-as-you-go model or on-demand. This type of system can be found in Microsoft Office’s 365, BigCommerce, Google Apps, Salesforce, Dropbox, MailChimp, ZenDesk, DocuSign, Slack, Hubspot.
- On-premise: software that’s installed in the same building as your business.
Cloud computing has grown into a vast and complex ecosystem of technologies, products, and services. More than one in four developers prefer to develop software on cloud platforms. Over half of all software testing, too, is now done in the cloud. This means the cloud can serve the IT specialist in the company by providing networking and infrastructure services with IaaS or Infrastructure as a Service. It can offer a sandbox for software development and testing for programmers with Platform as a Service or PaaS. It can even offer ready-to-use software applications that are directly used by end users via Software as a Service or SaaS. Each of these cloud computing service models offer users varying degrees of control, customization options and security.
The next evolution in delivering corporate cloud services is known as anything-as-a-service or XaaS. XaaS can deliver integrated hardware and software services over the internet, in one seamless package. XaaS (pronounced ‘Zaas’) is the next generation of cloud computing services which integrates the online delivery of separate private or public cloud services to users.
Hyper-scale Data Centers Set to Scale Up
In the digital age, businesses operate at a hectic speed. This is an era of instant consumption, and enterprises cannot wait for their information technology systems to deliver the services at a pace that traditional systems offer. Organizations need an IT infrastructure that can scale at an extremely quick pace to provision increased demand and then scale down appropriately when demand reduces. This has led to the demand for hyper-scale data centers.
Hyper-scale data centers are large, centralized facilities designed to support the rapidly growing demand for cloud computing services. These data centers are characterized by their ability to scale quickly and efficiently to accommodate large amounts of data and processing power, as well as the use of standardized, modular components and automated management systems.
As cloud computing continues to grow, the demand for hyper-scale data centers is also expected to scale up. This is because organizations are increasingly relying on cloud computing to support their digital transformation initiatives, such as data analytics, machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications. The scalability and cost-effectiveness of hyper-scale data centers make them an attractive option for organizations looking to leverage cloud computing for their business needs.
‘A Hyperscale (or Enterprise Hyperscale) data center is a facility owned and operated by the company it supports. This includes companies such as AWS, Microsoft, Google, and Apple.
They offer robust, scalable applications and storage portfolio of services to individuals or businesses. Hyperscale computing is necessary for cloud and big data storage.
Hyperscale data centers are significantly larger than enterprise data centers, and because of the advantages of economies of scale and custom engineering, they significantly outperform them, too. Not by any means an official definition, a hyperscale data center should exceed 5,000 servers and 10,000 square feet. What further distinguishes hyperscale data centers is the volume of data, compute, and storage services they process. In a survey, 93% of hyperscale companies expect to have 40 GigaBytes per second (Gbps) or faster network connections.
Due to the modularity of hyper-scale data centers, data center operators can replace individual physical components, which gives organizations extreme flexibility in scaling at the physical level, as components can be added modularly.
However, the growth of hyper-scale data centers also raises concerns about energy consumption, data privacy and security, and the potential for vendor lock-in. It’s important for organizations to carefully evaluate these factors when deciding whether to use hyper-scale data centers for their cloud computing needs.
Growing demand for cloud-based container system
An alternate to a virtual machine, the cloud-based container system as service, is in demand. It allows apps to be deployed in a quick and straightforward manner.Containerization creates abstraction at an OS level that allows individual, modular and distinct functionality of the app to run independently. As a result, several isolated workloads can dynamically operate using the same physical resources.
Using a containerization engine such as the Docker Engine, containers create several isolated OS environments within the same host system kernel, which can be shared with other containers dedicated to run different functions of the app. Only bins, libraries and other runtime components are developed or executed separately for each container, which makes them more resource efficient as compared to VMs.
The build it once, run it anywhere mantra of containers has found huge interest among organizations. It also delivers better infra security and allows quick releases of new software modules and features to run smoothly.As containers simplify deployment, management and operational concerns associated with a hybrid cloud, they are expected to see a huge rise in deployment, in line with the growth observed with respect to the hybrid cloud. It’s possible for CSPs to offer hosted container management services and at the same time segregate the platforms from each other using cloud container systems.
By 2023, Gartner predicts that more than 70 per cent of global organizations will be running more than two containerized applications in production, up from less than 20 per cent in 2019. Similarly, IDC predicts that 95 per cent of new micro-services will be deployed in containers by 2021. In a study by 451 Research found that by the year 2020, spending on containerization technologies will grow at a 40 percent compounded annual rate to reach the $2.7 billion mark.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is a cloud-computing execution model in which the cloud provider acts as the server, dynamically managing the allocation of machine resources. As with containers, serverless has enabled developers to focus on application development without worrying about underlying infrastructure considerations such as the number of servers, amount of storage, etc. Pricing is based on the actual amount of resources consumed by an application, rather than on pre-purchased units of capacity. It is a form of utility computing.
The real utility of “serverless computing” is simplicity because the server management and capacity planning decisions are completely hidden from the developer or operator.We’re witnessing a reengineering of public cloud services to use a serverless approach. First, we’re seeing resource-intensive services such as compute, storage, and databases, but you can count on the higher-end cloud services being added to the list over time, including machine learning and analytics. What this all means for the enterprise is that less work will be needed to figure out how to size workloads. This serverless trend should also provide better utilization and efficiency, which should lower costs over time. Still, be careful: I’ve seen the use of serverless computing lead to higher costs in some instances. So be sure to monitor closely, advises David S. Linthicum is a chief cloud strategy officer at Deloitte Consulting.
The Power of AI and Machine Learning in the Cloud
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning have emerged as game-changers in the realm of cloud computing. These technologies empower cloud platforms to analyze vast amounts of data and extract meaningful insights in real-time. AI and ML algorithms enable cloud services to enhance decision-making processes, automate tasks, and drive innovation. From predictive analytics to natural language processing, AI and ML algorithms have the potential to optimize cloud performance, improve efficiency, and offer personalized user experiences.
AI and Machine Learning (ML) are poised to revolutionize cloud solutions, as predicted by Gary Eastwood, an IDG Contributor. He envisions a fusion of AI and the cloud, where the vast amount of data stored in cloud servers can be accessed and utilized by AI systems to make decisions and learn. As the AI systems gain knowledge, they can share this newfound data with the cloud, enabling other AI systems to learn as well. This symbiotic relationship between AI and the cloud unleashes immense computational power and the ability to process and analyze large volumes of data.
Key players in the AI and ML space, such as IBM, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon Web Services, are already leveraging these technologies to deliver cloud-based services aimed at driving business growth. These tech giants recognize the potential of AI and ML in enhancing cloud capabilities and are actively incorporating them into their offerings. By combining the power of AI and ML with the scalability and resources provided by the cloud, these companies are paving the way for innovative solutions that can drive transformative changes across industries.
Edge Computing Moves to Center Stage
The rapid growth of connected devices and the immense volume of data they generate have propelled edge computing, also known as fog computing, to the center stage. According to surveys by Cisco and Gartner, the number of connected devices is expected to skyrocket, necessitating smaller data centers located closer to where data is generated. Edge computing enables the collection and processing of data at local computing devices, such as gateways, instead of relying on centralized cloud storage.
Predictions from Business Insider, Gartner, and IDC FutureScape highlight the significance of edge computing, stating that a substantial number of IoT devices will utilize fog computing a significant portion of enterprise-generated data will be stored at the edge, and a growing number of enterprises will invest in edge locations and co-location facilities to deliver digital services to local users and devices.
5G and Cloud
5G, the latest generation of cellular mobile communications, offers numerous advantages such as high data-throughput rates, reduced latency, energy savings, increased system capacity, and the ability to connect a massive number of devices simultaneously. One significant impact of 5G is its ability to bring cloud computing to a wider audience. This allows businesses to leverage cloud-based systems to automate processes, enhance IoT device connectivity, enable data analytics for better insights, and provide online training for employees regardless of their location. The combination of 5G and cloud computing opens up new possibilities and opportunities for businesses to streamline operations, improve productivity, and stay competitive in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Global Cloud Computing Market
The global Cloud Computing Market size was valued at $545.8 billion in 2022 and it is projected to reach $1,240.9 billion by the end of 2027, growing at a CAGR of 17.9%.
Several factors facilitate the growth of the cloud computing market. Here are some of the prominent drivers of cloud computing market growth.
1. Increased ROI with Lower Storage and Infrastructure Costs
The implementation of cloud computing enables organizations to lower their storage and infrastructure costs while enhancing returns. With the adoption of cloud computing, enterprises do not have to worry about setting up infrastructure for storing huge volumes of data. Moreover, the pay-as-you-go model of the cloud allows enterprises to pay only for the cloud services they use. All these factors contribute to the cloud computing industry’s growth significantly.
2. Increased Adoption of Hybrid Cloud
Another factor that contributes to the growth of the cloud-based computing market size is the increasing adoption of hybrid cloud. Hybrid cloud services provide several benefits to enterprises. The most significant benefits include increased compliance and security, efficient integration, and better workload management. Moreover, it also offers greater flexibility to switch to the cloud platform. Therefore, there has been an increase in the hybrid cloud market growth in recent times.
Restraints and Challenges of Cloud Computing Market Size
No doubt, there are several factors that will accelerate the growth of the cloud computing market size in 2023. However, some factors limit growth. Here are some major factors that impede the growth of the cloud computing market.
1. Cybersecurity Attacks
One of the major limiting factors is the increase in cybersecurity attacks around the globe. Cloud computing provides plenty of benefits to businesses. It also has appropriate measures in place to secure the important data of the enterprises in the best possible way. However, the data that are stored on the cloud are prone to potential cyberattacks. Some prominent cyberattacks include cloud malware injection attacks, service hijacking, Meltdown, Spectre, and man-in-the-cloud attacks. All these cyberattacks can make enterprise data vulnerable and incur a huge loss for businesses. That is why many businesses are not willing to adopt cloud computing owing to the security of their data.
2. Complex Regulatory and Compliance Needs
In recent times, it has become mandatory for businesses to meet the increasing compliance and regulatory needs. However, the compliance and regulatory requirements have become more complex over the years. It becomes difficult for businesses to meet compliance needs. Therefore, many enterprises show reluctance to adopt cloud computing to avoid legal penalties.
Segments
The cloud computing market ecosystem consists of several segments. The global market of cloud computing is divided based on deployment, end-use, enterprise size, and region.
Because of deployment, the cloud computing market is divided into private deployment and hybrid deployment.
As per the cloud computing growth forecast, the revenue share of the private deployment segment was more than 46% in the year 2021. The hybrid deployment segment is anticipated to experience significant growth in the coming years.
The hybrid deployment segment is anticipated to register the second-fastest CAGR from 2021 to 2028 owing to the growth of cloud and industrialized services and decrease in traditional Data Center Outsourcing (DCO)
Moreover, along with the flexibility to move workloads between private and public deployment depending on the computing needs, a hybrid deployment is expected to provide enterprises more data deployment options in the long run
A recent study from Bain & Co, KPMG and Statistica says that as long as cloud is growing, it’s natural for Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), function as a service (FaaS), backend as a service (BaaS) to grow aggressively too. SaaS is a software license service on a subscription basis and it’s hosted centrally. Currently, this sector is influenced by key players like Google Apps and Salesforce, and new companies are likely to jump in the competition.
The growth rate for SaaS is predicted to be 18% CAGR by 2020. The PaaS offers a safe platform which gives customers a chance to develop, launch and manage applications in a modest way rather than having to build and maintain the infra by yourself. The growth rate of PaaS has been remarkable; it has been predicted that the adoption rate will escalate from 32% in 2017 and is supposed to reach 56% in 2020. IaaS provides a virtual resource service on the web and is dominated by Google Compute Engine (GCE), Azure, Amazon Web, AWS and IBM Bluemix. IaaS market is predicted to go over $17B in 2018. We saw positive performance in cloud sector services. Hence, we can expect greater cloud sector growth in 2018 and later.
The IaaS segment is expected to register the highest CAGR over the forecast period owing to the increased adoption of multi-cloud due to benefits, such as scalability and fast data accessibility
Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs) is anticipated to emerge as the fastest-growing segment from 2021 to 2028 due to high demand for cloud computing in SMEs owing to reduced costs of IT hardware and software, improved processing capacity and elasticity of storage, and greater mobility of access to data and service
Since end-use, the cloud computing market has been divided into IT & Telecom, BFSI, manufacturing, government and public sector, retail and consumer goods, energy and utilities, healthcare, and media and entertainment.
The manufacturing end-use segment is expected to register the highest growth rate over the forecast period. Owing to various functionalities, cloud computing aids manufacturers in utilizing multiple types of production systems, ranging from High-Performance Computing (HPC) and 3D printing to IoT and industrial robots
Based on the enterprise size, the global cloud computing market is divided into large enterprises and small and medium-sized enterprises.
Geographical outlook
On the basis of region, the global market of cloud computing includes North America, South America, Europe, Middle East & Africa, and Asia Pacific region. North America is expected to dominate the global market owing to the early adoption of the latest technologies in the region.
North America is home to some of the biggest technology companies such as Google, Microsoft, and IBM and this factor has enabled the region to boast a market size of USD 61.59 billion in 2019. Moreover, the regulatory and research environment in the region is extremely favorable for development and adoption of advanced cloud technologies based on Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). As a result, North America is slated to dominate the cloud computing market share during the forecast period. Increasing penetration of the internet and rising usage of smartphones will aid Asia-Pacific register a high CAGR, while rapid deployment of 5G will favor market growth in Latin America and Middle East & Africa.
While technology spending in APAC has increased, the setback due to the recent COVID-19 pandemic is imminent. The cloud technology adoption is expected to increase in sectors where the WFH initiative is helping to sustain enterprise business functions.
Asia Pacific is expected to emerge as the fastest-growing regional market over the forecast period owing to the increasing focus of SMEs and large enterprises to enhance their digital initiatives
The growth in the IT services industry in markets, such as India, China, and other South Asian regions, is also expected to propel the regional market growth over the forecast period
Market leaders
Some of the Key Players in the Cloud Computing Market are: Adobe, Inc.; HCL Technologies; SAP SE;VMware, Inc.; The International Business Machines Corporation (IBM); Amazon Web Services (AWS); Hewlett-Packard Company (HPE); Salesforce.com; Rackspace, Inc.;
Microsoft Corporation; Oracle Corporation
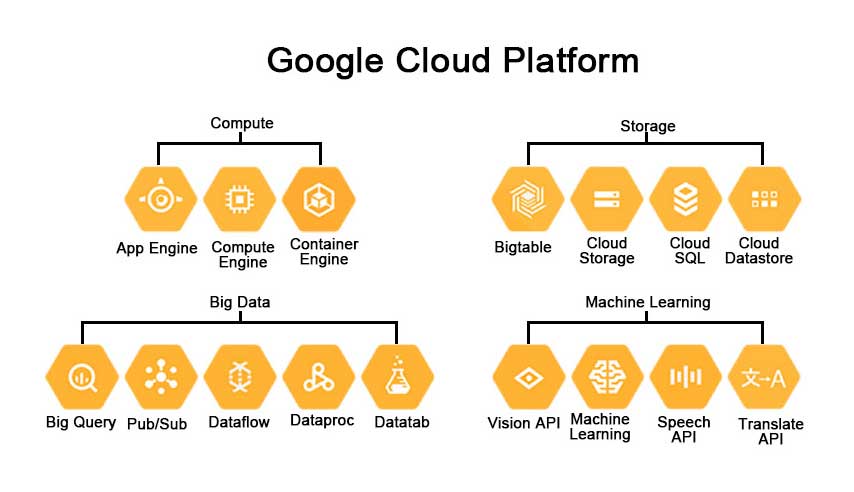
Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are the dominant players, with emerging companies like IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud, Salesforce, and Alibaba also competing in the market. AWS remains a leader with a wide range of services, while Azure offers the Microsoft Azure Machine Learning Service for cloud-based machine learning model development. Google Cloud Platform has gained traction through partnerships and acquisitions, while Salesforce excels in CRM and AI-powered sales opportunities. IBM focuses on open technologies, hybrid cloud solutions, analytics, and enterprise development. Alibaba Cloud targets the Chinese market and aims to match or surpass AWS in terms of customers and technology. Oracle and SAP are investing in IoT-related advancements to streamline their products and services. Overall, the cloud market continues to evolve with intense competition and a focus on innovative solutions and technologies.
Revolutionizing Industries with Cloud Convergence
The convergence of AI, Machine Learning, IoT, and 5G is reshaping various industries and transforming the way businesses operate. In healthcare, cloud-powered AI can analyze patient data to assist in diagnostics, predict disease outcomes, and support personalized treatment plans. Smart homes leverage IoT devices connected to the cloud, providing enhanced security, energy efficiency, and convenience. Industries like manufacturing benefit from the integration of AI and IoT with cloud computing, enabling predictive maintenance, optimizing production processes, and improving overall efficiency.
Challenges and Future Implications
While the convergence of AI, Machine Learning, IoT, and 5G presents remarkable opportunities, it also brings forth challenges. Ensuring data security, addressing privacy concerns, and managing the complexity of integrating these technologies are critical aspects that need attention. However, as advancements continue, the potential for innovation and transformation cannot be overstated. The cloud computing landscape is set to witness a surge of novel applications, services, and possibilities.
Conclusion
The convergence of AI, Machine Learning, IoT, and 5G is revolutionizing the cloud computing landscape. This amalgamation offers unprecedented capabilities, enabling real-time data analysis, seamless device connectivity, and powerful insights. As industries continue to harness the power of this convergence, we can expect transformative changes in healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and many other sectors. The cloud is no longer just a storage and computing platform—it has become the foundation for a smarter, more connected future, driven by the synergistic power of AI, Machine Learning, IoT, and 5G.
References and Resources also include:
https://www.esds.co.in/blog/cloud-computing-trends-driving-growth-2018/#sthash.4CQ2lCAU.dpbs
https://www.esds.co.in/blog/cloud-computing-iot/#sthash.QoYpxpRN.dpbs
https://www.techaheadcorp.com/blog/top-cloud-service-providers/
 International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis