Human-centric technology refers to technology that is designed with a focus on the needs and preferences of human users. This approach to technology development aims to create products and systems that are intuitive, easy to use, and enhance the human experience.
Human-centric technology is designed to be accessible to as many people as possible, including those with disabilities or limitations. This promotes inclusivity and ensures that everyone can benefit from technological advancements.
The need for human-centric technology is going to further increase in the future when you consider that by 2050, the world’s population aged 60 years and more will most likely cross 2Bn. In the US, there will be 75% increase in the number of senior citizens needing assisted living. Imagine a digital home that proactively but sensibly supports people in their daily lives and provides the needed care for the elderly through human-centric technology.
Ambient Intelligence (AmI) is a concept in computer science and engineering that refers to an environment in which everyday objects are connected and integrated with technology to provide intelligent, context-aware, and personalized services to users. It involves the use of sensors, embedded systems, artificial intelligence, and other technologies to create an intelligent environment that can adapt to users’ needs and preferences.
AmI aims to create a seamless and unobtrusive integration of technology into the physical environment, allowing devices and systems to interact with users in a natural and intuitive way, without the need for explicit commands or interfaces. The goal is to create an environment that can anticipate and respond to users’ needs and desires, making their lives more comfortable, efficient, and enjoyable.
Examples of AmI include smart homes, where devices and appliances are interconnected and can be controlled by voice or gesture, smart cities, where traffic, lighting, and public services are optimized using real-time data, and healthcare systems that can monitor and respond to patients’ needs in real-time
“The most profound technologies are those that disappear. They weave themselves into the fabric of everyday life until they are indistinguishable from it.”- Late Mark Weiser, who was the chief scientist at Xerox PARC. We are poised for such a dramatic disruption in the way we live in our homes through ambient Intelligence.
For more information about Ambient intelligence (AmI) technology and applications please visit : Ambient Intelligence: Technology that Adapts to Our Environment
Ambient intelligence (AmI) technology
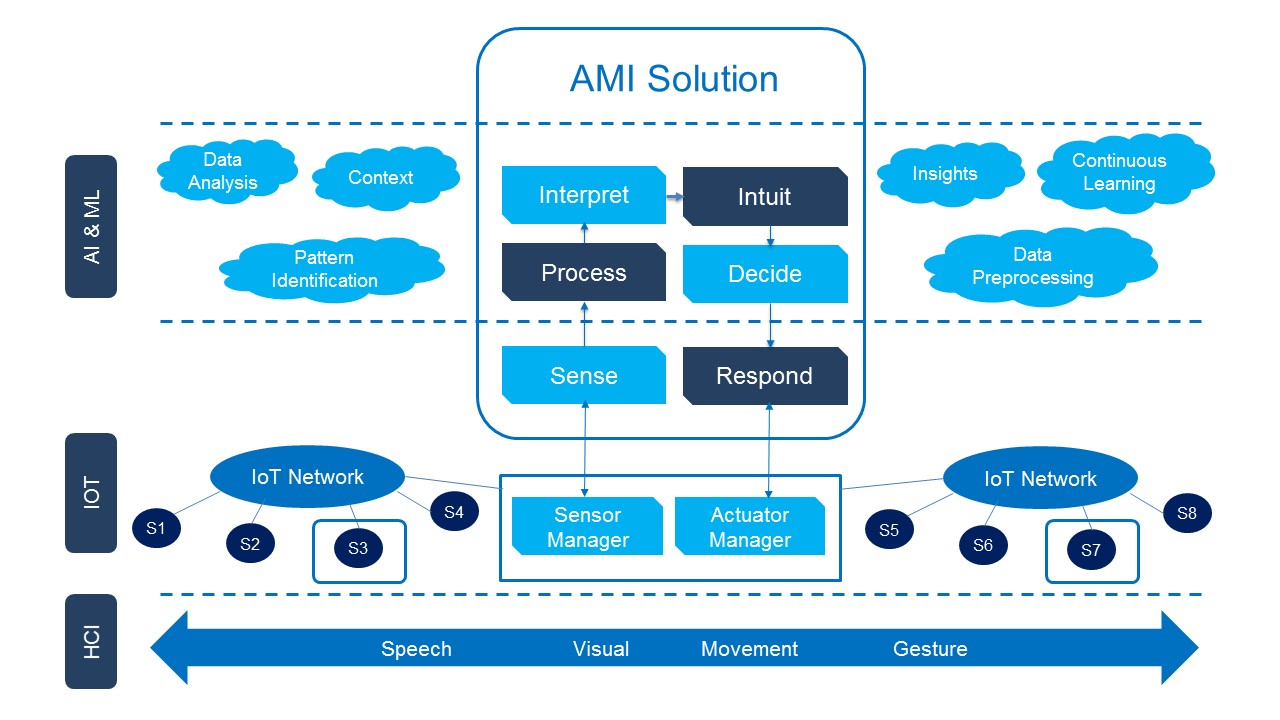
Ambient intelligence (AmI) represents the future vision of intelligent computing where explicit input and output devices will not be required; instead sensors and processors will be embedded into everyday devices and the environment will adapt to the user’s needs and desires seamlessly. AmI systems, will use the contextual information gathered through these embedded sensors and apply Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques to interpret and anticipate the users’ needs. The technology will be designed to be human centric and easy to use.
The ability of technology to take decisions and act on our behalf taking into consideration our preferences based on the data available to it from all the connected sensors and systems surrounding the user can be defined as Ambient Intelligence or AmI.
AmI is multi-disciplinary and works at the intersection of several technologies including Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, Internet of Things (IoT), Pervasive-Ubiquitous Computing, Networks and Human Computer Interaction (HCI).
AmI senses the environment and user context through various intelligent digital systems installed in our homes or workplaces, utilizing different IoT sensors and devices. After that, the AmI system processes the data collected from these systems. Once data is processed and analyzed, the AmI system interprets it to understand user proximity, state, intent, and behavior. It then intuits through insights derived from the current data, prior learnings and pattern identification. It then decides the next best action and responds back to the user through an intuitively designed natural interface of a smart device.
References and Resources also include:
 International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis