Digital battlefields, hybrid warfare, and the future of threat intelligence
IDST Intelligence Briefings
(Latest Security & Cyber Videos)
Why This Magazine Exists
Security, Cyber & Counter-Threats examines the evolving landscape of modern security in an era defined by digital conflict, hybrid warfare, and persistent global threats.
From cyber operations, information warfare, and intelligence-driven defense to counter-terrorism, internal security, and emerging threat vectors, this magazine provides strategic analysis, technical insight, and policy-relevant perspectives for decision-makers, practitioners, and researchers navigating an increasingly contested security environment.
What We Track
- Cyber warfare & cyber defense
- Information operations & influence campaigns
- National security threat assessments
- Emerging digital and hybrid warfare doctrines
- Critical infrastructure & cyber resilience
Latest Analysis & Intelligence
-

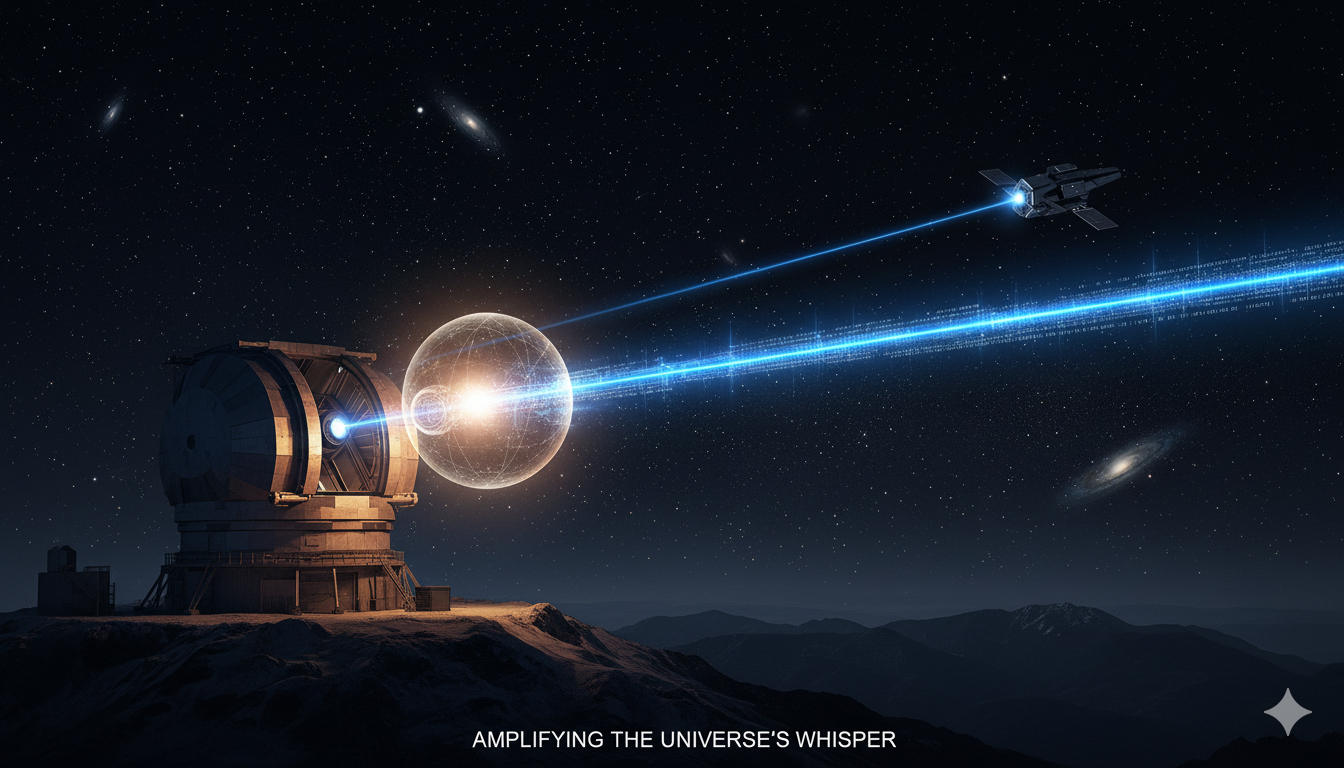
The Silent Amplifier: A Quantum Leap for Bringing Data Back From Deep Space
Imagine receiving a high-definition video, sent in real-time from a rover on Mars or a probe orbiting Jupiter. For decades, space communication has relied on radio waves—a trusted but limited technology, offering data rates more akin to a dial-up modem than modern fiber optics. The future, however, lies in light. Optical communication, using lasers…
-

The U.S. Army’s New Cybersecurity Arsenal: How Software Bills of Materials Are Fortifying National Security
In today’s digital battlefield, lines of code are becoming as critical as frontline troops. Recognizing this, the U.S. Army is deploying a powerful new tool against cyber threats: the Software Bill of Materials (SBOM). With cyber incidents in the Department of Defense continuing to rise and software supply chain attacks projected to multiply in…
-

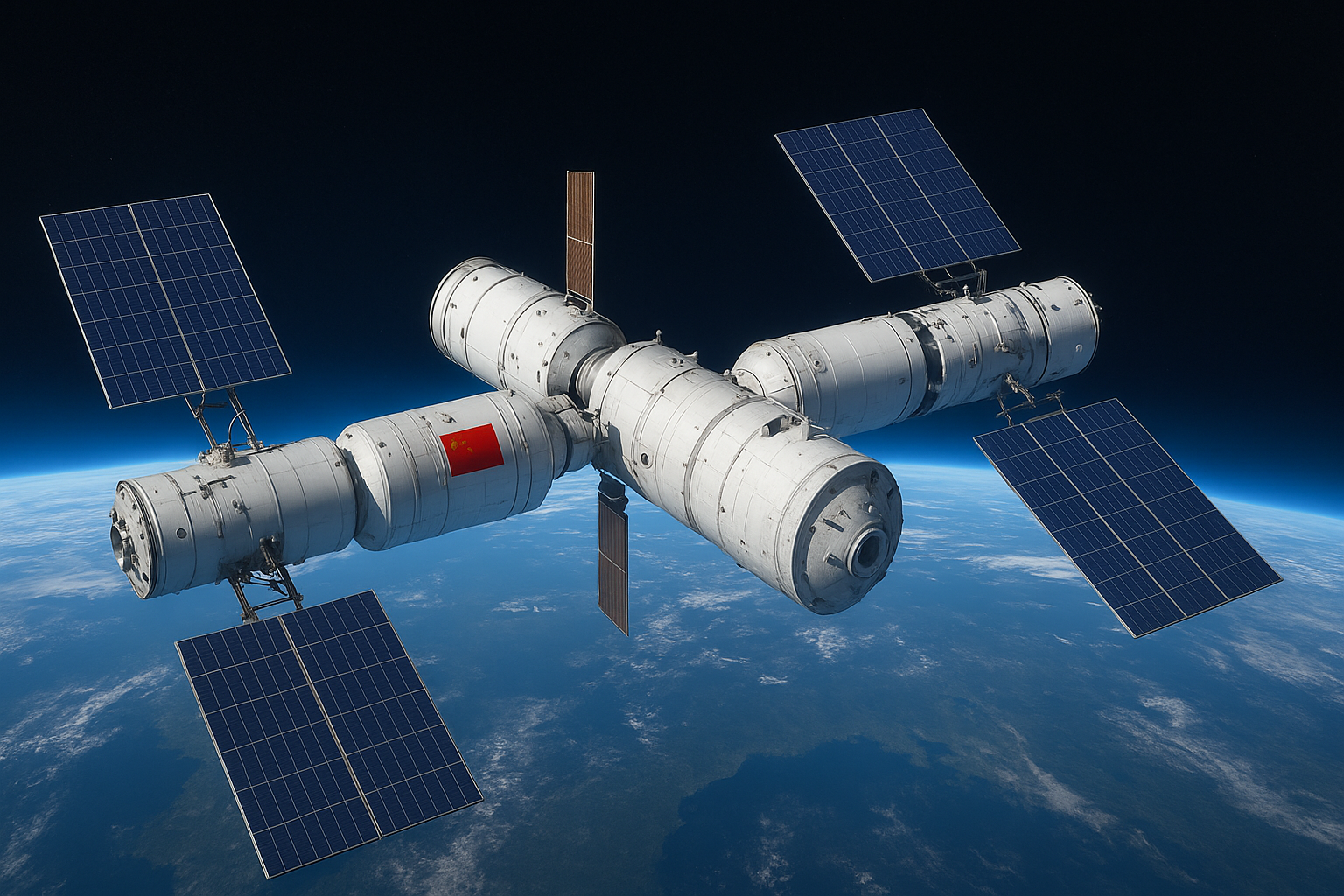
China’s Tiangong Space Station: A New Pillar for Science and Global Cooperation in Orbit
Soaring roughly 240 miles above Earth, China’s Tiangong Space Station—whose name translates to Heavenly Palace—represents far more than a triumph of engineering. It is a defining symbol of China’s emergence as a leading spacefaring nation. As the second fully operational and continuously crewed space station after the International Space Station (ISS), Tiangong stands as a…
-

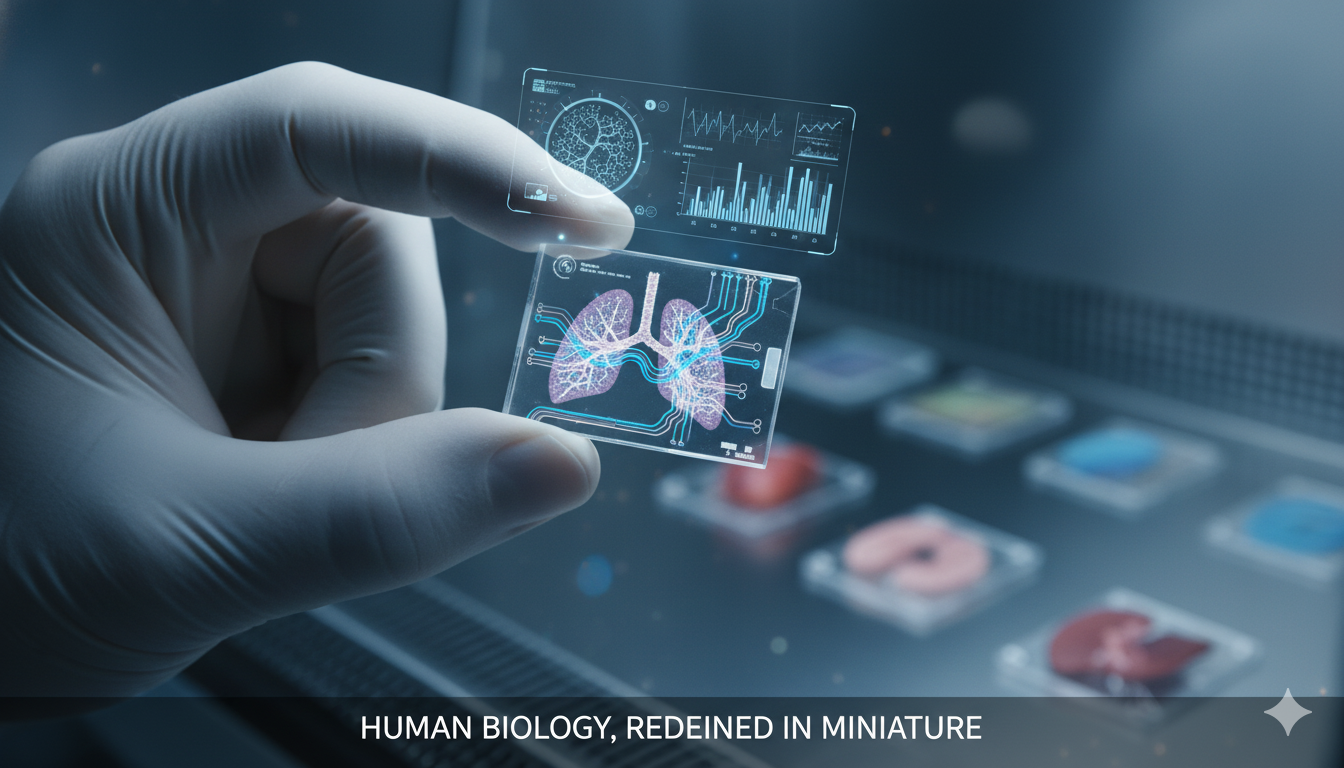
The Organ-on-a-Chip Revolution: How Micro-Organs Are Transforming Medicine and Saving Lives
Imagine a future where testing a new drug doesn’t require animal trials that often fail to predict human responses. Where instead of waiting for a life-saving organ transplant that may never come, patients could receive new organs grown from their own cells. While the dream of full-sized bioprinted organs remains on the horizon, a remarkable…
-

Beyond Glass: Next-Generation Backsheets Empowering the Future of Solar Technology
When we think of a solar panel, the focus often falls on the visible solar cells that capture sunlight. Yet, tucked behind these cells lies a critical component that quietly ensures the panel’s performance, safety, and longevity: the backsheet. Acting as the module’s protective shield, the backsheet forms the last line of defense against…
-

The Military Tank Container Market: Fueling Global Defense Logistics with Strategic Growth
In the domain of military logistics, one niche with growing strategic importance is the market for military-grade tank containers—containers designed for transporting liquids, gases, or hazardous bulk materials under rugged, expeditionary, and secure conditions. This market is increasingly underpinning global defense supply chains. Recent market estimates place the sector’s value at approximately USD 1.35 billion in 2024…
-

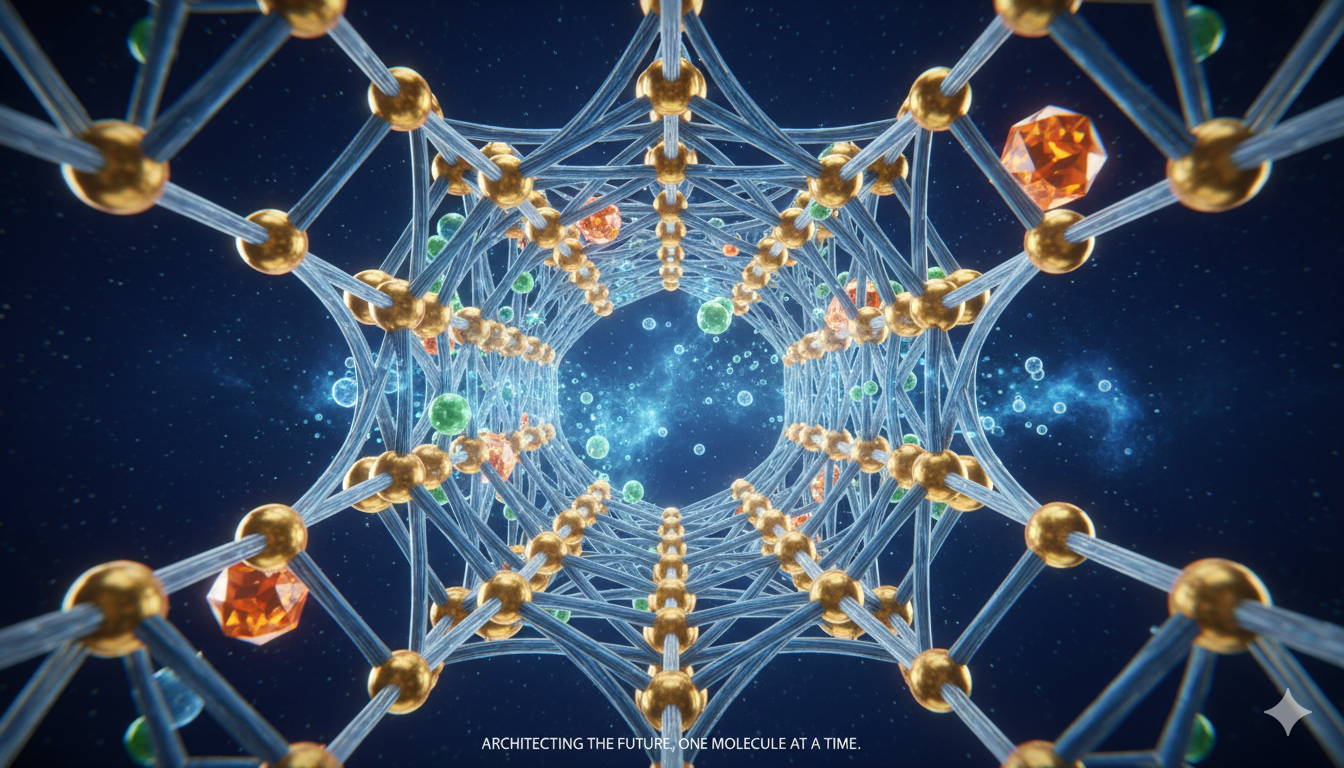
Metal-Organic Frameworks: The Architecture of a Sustainable Future
Introduction From the microscopic world of atoms to the macroscopic challenges of climate change, chemistry has long been the bridge between scientific understanding and practical innovation. Modern materials science has opened new frontiers in designing substances with precision at the molecular level — structures that not only serve human needs but also reflect an…
STRATEGIC SUB-MAGAZINES
Modern military power emerges from the interaction of platforms, people, doctrine, and integration across domains. The Defense & Military Systems magazine is structured into focused sub-magazines that examine how combat capability is built, sustained, and employed across air, land, sea, weapons, and human systems.
Cyber & Information Warfare
Industrial outcomes are shaped as much by incentives, policy, and market structure as by engineering. Price signals, investment cycles, and regulatory frameworks quietly determine which technologies scale, stagnate, or fail.
This sub-magazine examines how markets behave under strategic pressure—where capital flows, how demand signals distort decisions, and why some industries adapt faster than others.
Explore the Cyber & Information Warfare Sub-Magazine →
Security & Threat Management
Modern security is defined by persistence, coordination, and anticipation. This sub-magazine focuses on how threats are identified, mitigated, and managed across institutions, infrastructures, and societies.
Explore the Security & Threat Management Sub-Magazine →