In his series of books Science and Civilization in China, Joseph Needham, a British science historian, described China as a great country of invention and creation that fell behind in modern times. But that situation is changing rapidly, and now Chinese are working in almost every field of science and technology, from internet development to brain studies, from probing space to exploring the deep ocean, from observing the universe to researching micro particles. China has now transitioned from a technologically backward but technically advanced civilization-state to a technologically-advanced nation-state.
The Global Innovation Index (GII) ranks world economies according to their innovation capabilities. Consisting of roughly 80 indicators, grouped into innovation inputs and outputs, the GII aims to capture the multi-dimensional facets of innovation.
China now ranks 12th among the 132 economies featured in the GII 2021 moving up 2 places from its 14th place in 2020, establishing itself as an innovation leader. China produces more innovation outputs relative to its level of innovation investments. China ranks 25th in innovation inputs, higher than both 2020 and 2019. As for innovation outputs, China ranks 7th. This position is lower than both 2020 and 2019.
China stands out for producing innovations that are comparable to those of the high-income group, including the top 10 economies, such as the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and the United States of America. It maintains its world leadership in several indicators related to intellectual property: Patents by origin, Utility models, Trademarks, and Industrial designs. It also ranks within the top three economies in other indicators, such as Productivity growth and Creative goods exports.
China also retains 1st place in the quality of innovation among middle-income economies for the eighth consecutive year. In the indicators that compose this GII metric, China ranks 3rd in the Quality of universities, with Tsinghua University, Peking University, and Fudan University within the top 50 universities worldwide. It is also the middle-income economy that makes the greatest efforts in the internationalization of its inventions: patent families account for 10% of China’s innovation quality score, much higher than the average for middle income economies, which is set at 4%. China hosts 17 of the top science and technology clusters worldwide – with Shenzhen–Hong Kong–Guangzhou and Beijing taking the 2nd and 4th spots, respectively.
The U.S.’s pre-eminence among the world’s top research universities continues to diminish, according to a new global ranking, while mainland Chinese universities are on the rise, producing a greater quantity and higher quality of research than ever before. According to World University Rankings, released in 2022 by Times Higher Education, The U.S. and U.K. continue to dominate the upper echelon of the rankings, with the U.S. taking seven of the top 10 slots and Britain three. But among the top 100 universities, the number of those in the U.S. fell to 34 from 43 between 2018 and this year. The number of universities in mainland China, which excludes Hong Kong, in the top 100 increased from two to seven.
“The data is very clear: America can no longer take for granted its decadeslong dominance of world higher education and research, and it is China that is leading the challenge,” said Phil Baty, the rankings editor. “If current trends remained the same, we would see China overtaking the U.S. in the coming years.”
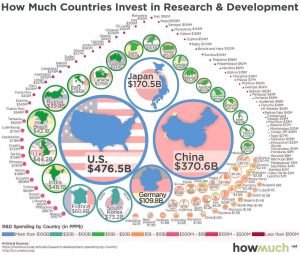
The gap in research and development (R&D) funding between the United States and China is closing fast. According to a National Science Foundation (NSF) report from April 2022, while the United States remains the global leader in R&D spending ($708 billion in 2020), China’s R&D spending was not far behind, reaching $526 billion in 2020. As per the NSF report, “the average annual rate of increase in China’s R&D total (10.6% from 2010–19) continues to greatly exceed that of the United States (5.6%).” This surge in funding is geared towards meeting China’s Innovation Strategy, directed by its “Made in China 2025” strategy.
“The year-to-year growth in R&D spending indicates firm governmental and social support for making China a scientific power,” says Xie Xuemei, a specialist in innovation economics at Shanghai University in China. “However, there is still a long way to go” to match the research capabilities of developed countries, she adds.
Moreover, compared to other high-technology economies, less of China’s R&D spending has been geared towards the theoretical sciences—often referred to as “basic” sciences—that can prepare the ground for the invention of disruptive technologies. Basic research expenditures were also up, hitting 97.55 billion yuan ($14.1 billion), an increase of 18.5%. For comparison, the United States spent $86.32 billion on basic research in 2016, according to OECD. China’s R&D spending through its various forms of enterprises and government institutions is heaviest in experimental R&D, which is on the most applied side of the innovation spectrum. That type of innovation focuses on such areas as process improvement in manufacturing and consumer-focused technological developments. A national innovation strategy that strives to harness R&D to economic growth has been driving the increase in both government and industrial R&D spending in recent years, Xie says.
In 2016, For the first time, China overtook the United States in terms of the total number of science publications, according to statistics compiled by the US National Science Foundation (NSF). China published more than 426,000 studies in 2016, or 18.6% of the total documented in Elsevier’s Scopus database. That compares with nearly 409,000 by the United States.
Data compiled by Japan’s National Institute of Science and Technology Policy discovered that China leads the field in terms of the most cited science papers (27.2 percent) compared to the U.S. (24.9 percent) in 2018, 2019, and 2020. In the period 2018 to 2020, China overtook the U.S. in the number of peer reviewed scientific papers published in scientific journal articles annually (407,181 compared to 293,434). While some tend to question the quality of these Chinese publications, their dissent appears more opinionated than factually based, and perhaps underestimates China’s growing science capabilities.
China is also quickly becoming a leader in STEM (science, technology, engineering, math) Ph.D.s as per data compiled by the Georgetown University’s Center for Security and Emerging Technologies. The center’s report, titled “China is Fast Outpacing U.S. STEM PhD Growth,” indicates that from being behind the U.S. in 2000 – with Chinese universities granting 9,098 STEM Ph.D.s compared to the United States’ 18,209 that year – China overtook the U.S. a decade later, granting 34,801 STEM Ph.D.s compared to U.S. universities granting 26,076 in 2010. In 2019, Chinese universities granted 49,448 STEM Ph.D.s compared to U.S. universities producing 33,759. The report suggests that by 2025, China will have double the number of STEM Ph.D. graduates of the United States.
Moreover, China has the world’s largest number of R&D personnel, and ranks second in the world in the number of scientific papers published in international journals. Scientific and technological advances contribute 55.3 percent of China’s economic growth. (China Daily). Statistics show that Chinese investment in research and development in 2016 exceeded that of the entire European Union and was second only to the US, accounting for 21 percent of the global total.
China moved into second position as filer of international patent applications at WIPO in 2017, closing in on the US as long-time leader, in another record year in the use of WIPO’s intellectual property services for patents, trademarks and industrial designs. Two Chinese technology companies were the top filers of international patent applications in 2017, with Huawei, number one filer and ZTE at two, followed by Intel, Mitsubishi and Qualcomm. World International Property Agency says based on 2017 data, China will overtake US in three years. This is part of a shift in the geography of innovation, with almost half of all WIPO filings now coming from east Asia.
China has become the world’s largest source of new patents, industrial designs and trademarks. According to the World Intellectual Property Organisation, China in 2014 filed 34 per cent of the world’s patents, compared with 22 per cent for the US and 12 per cent for Japan. China also filed 50 per cent of the world’s new industrial designs, against 9 per cent for the US; and 76 per cent of new trademarks, compared with the US’ 13 per cent.
“The US continues to be the global leader in science and technology, but the world is changing,” says Maria Zuber, a geophysicist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge. As other nations increase their output, the United States’ relative share of global science activity is declining, says Zuber, who chairs the National Science Board, which oversees the NSF and produced the report. “We can’t be asleep at the wheel.”
China’s technology advancements
Chinese President Xi Jinping said in a speech, “A new generation of technology represented by artificial intelligence, quantum information, mobile communications, internet of things and blockchain is accelerating breakthrough applications”. Since entering the 21st century, global science and technological innovation has entered into an unprecedented period of intensive activity. “A new round of scientific and industrial revolution is reconstructing the global innovation map and reshaping the global economic structure.” Xi also emphasized the need for China to focus on technological development and become the global center of science and innovation.
China is making rapid advancements in many technologies thus narrowing its gap with western world. Former US energy secretary Steven Chu has even observed that China is ahead of America in areas ranging “from wind power to nuclear reactors to high-speed rail”. China is also catching up fast in artificial intelligence, genetic engineering, 5-G broadband technology and the “Internet of Things.” Some of its achievements include a gigantic 500m-aperture spherical telescope, the launch of the world’s first hacker-proof quantum satellite and the development of world’s fastest supercomputer – the new Sunway Tianhe-1A. China has also developing twin high-performance fifth-generation stealth fighters, , and large number of missiles including “Carrier killer” missile, anti-ship cruise missile, nuclear submarine and long-range intercontinental missile. Its homegrown aircraft carrier is nearing completion.
Chinese scientists are actively participating in the research on machine learning and neuroscience, on biogenetics, on nanotechnology—and their findings are entering the commercial domain. Moreover, Chinese e-commerce firms such as Alibaba, JD.com and Pinduoduo are the technological equals of several foreign rivals, and China’s social media giants such as Tencent (creator of the social messaging WeChat app) and Alibaba (which introduced the Wangxin app popular with its Taobao user base) are no less innovative. In fintech, there is an increasing use of crypto-currencies and blockchain, and central bank digital currency.
China leads the world in 5G development with huge investment, rich variety, affordable models and wide-range applications, industry officials said at MWC Shanghai 2021, Asia’s biggest telecommunications show. Chinese telecom operators have invested more than 400 billion yuan ($59.4 billion) into 5G so far, driving a cumulative economic output of about 8.56 trillion yuan, which highlights the robust role that new network infrastructure plays in buoying economic growth, experts said.
China has more than 1.85 million 5G base stations as of June, already the world’s largest network. The number is expected to hit 3.64 million by the end of 2025, as the nation aims to have 26 5G base stations for every 10,000 people by then, according to a five-year plan unveiled earlier by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. According to the Wall Street Journal opinion piece, “America is far behind in almost every dimension of 5G while other nations — including China — race ahead. America’s average 5G mobile internet speed is roughly 75 megabits per second, which is abysmal. In China’s urban centers 5G phones get average speeds of 300 megabits per second.”
There are 218 5G models available on the market and over 90 percent of new middle and high-end smartphones (costing over 2,000 yuan) sold in China support 5G, according to Liu Liehong, vice minister at the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. The technology has played its part in China’s fight against the pandemic and in space, mines, hospitals, harbors and factories, Liu said at the event’s opening ceremony.
Chinese quantum computing researchers recently disclosed that a 60-qubit superconductivity quantum computing system with 99.5 percent fidelity could be achieved this year, and in 10 years, the system could evolve into a million-qubit level with a 99.8 percent fidelity.
China space advances boosting its technology innovation
China is becoming formidable space power, it has sent 10 astronauts into orbit over the last 13 years, launched its first moon probe and two space stations (Tiangong 1 and 2). Most recently, China launched the Shenzhou XI manned spacecraft with two astronauts to the Tiangong II space lab for a 30-day manoeuvre. China Chang’e 5 landed on the moon and return with samples, in first such attempt, officials said.
China is fast becoming a major space power as both its technology and launching frequency of satellites are improving at a rapid rate. China has launched more satellites than any other country in 2020 as of Sept. 30, according to a report by Bryce Space and Technology. China has conducted the greatest number of space launches in 2018 and 2019, and last year (2020) it has already launched 36 space vehicles out of a planned 40.
The country set a milestone in space exploration by landing its Chang’e-4 probe on the far side of the moon in January 2020. On 1st December 2020, China has landed Chang’e 5 Moon lander on the moon and has returned to Earth with the cargo of rock and “soil” it picked up off the Moon. It’s more than 40 years since the American Apollo and Soviet Luna missions brought their samples home. China is also working toward sending astronauts to the Moon and, eventually, Mars. It has also recently launched a re-usable ‘Space Plane’.
In a cave in Wuhan, capital of Central China’s Hubei Province, scientists from HUST have measured the gravitational constant for more than 30 years, and recently obtained the most accurate result ever. Isaac Newton discovered the principles of gravity more than 300 years ago, but the measurement of the gravitational constant had always been inaccurate. “The precise measurement of the gravitational constant is important for deeper understanding of gravity, and the measuring technology could be applied in navigation and the search for mineral deposits. The study might also help us figure out whether the universe has additional dimensions as surmised by Stephen Hawking, which might enable humans to traverse space and time,” Tu Liangcheng, director of HUST’s gravitation center, said.
China has built the world’s largest single-dish radio telescope the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope – in Guizhou province, which has discovered dozens of new pulsars. Scientists at China’s Purple Mountain Observatory and other institutions are pushing forward the construction of an observatory on the inland icecap in Antarctica. “That will definitely be a world leader,” said Shi Shengcai, director of antarctic and radio astronomy at the observatory.
China possesses the most rapidly maturing space program in the world and is using its on-orbit and ground-based assets to support its national civil, economic, political, and military goals and objectives. China has invested in advanced space capabilities, with particular emphasis on satellite communication (SATCOM), intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR), satellite navigation (SATNAV), and meteorology, as well as manned, unmanned, and interplanetary space exploration.
China’s space successes are also boosting its innovation in other fields such as Quantum satellite. China launched Quantum Satellite in 2016, which has conducted several prominent experiments, including facilitating a hacking-resistant video conference between Beijing and Vienna. It created a record-breaking communications link using entangled particles between satellites and an earth station. In the latest of a series of technological firsts attributed to the Micius Project, Chinese scientists have succeeded in establishing a secure link between two ground stations, separated by over 1,100km.
Innovation Challenges
Despite these advances, China’s effort at catching up to the production methods employed by the world’s most technologically advanced countries remains incomplete. The United States, the EU, Japan, and South Korea are well ahead in a number of fields. While China is the world’s largest market for automobiles, its foreign counterparts in joint-ventures, such as Volkswagen and GM, have largely retained the lead with respect to the embedded technology, product quality, production efficiency, and brand image of their produced goods.
China is a major supplier of active pharmaceutical ingredients and of generic medications, but indigenous innovation is on a modest scale with researchers now mobilizing artificial intelligence to create new drugs. As demand for the India-made COVID-19 vaccines gathers pace in foreign countries, even China seems to have grudgingly conceded that India’s COVID-19 vaccines are good, reports The Pharma Letter’s local correspondent. In a report in the China Communist Party’s mouthpiece, experts note that India’s plans to export the vaccine “could be good news for the global market given India’s competitive vaccine research and production capacity” and that “India’s vaccines are no less competitive than Chinese COVID-19 vaccines in both research and production capacity, considering that India has the world’s largest vaccine manufacturer and lower costs in labour and facilities.”
Producing commercial jet aircraft is another area that is posing a challenge to Chinese manufacturers, even though they enjoy the support of foreign producers of parts and modules.
While many U.S. and other countries’ firms have offshored labor-intensive parts of their integrated circuit production to China, they are manufacturing more utility-level products there that are designed for integration into consumer electronic devices, not cutting-edge technologies
China still imports 90 percent of its semiconductor components even though the industry became a national priority in 2000. Recently the Trump administration slapped a $1 billion fine on ZTE, which employs 75,000 people and is the world’s No. 4 maker of telecom gear, and to allow monitors to set up shop in its headquarters. In return, the company — once a symbol of China’s progress and engineering know-how — will be allowed to buy the American-made microchips, software and other tools it needs to survive. The recent ZTE incident made us see clearly that no matter how advanced our mobile payment is, without mobile devices, without microchips and operating systems, we can’t compete competently,” Pony Ma, chief executive of the Chinese internet giant Tencent Holdings said at a science forum.
China is positioned in the third tier of a four-tier global manufacturing hierarchy and is at least 30 years away from achieving its goal of becoming a strong manufacturing power, a senior official said on the sidelines of the two sessions in March 2021. China’s manufacturing industry has made marked progress lately, but the general view that it is “big, but not strong” and “comprehensive, but not excellent” has not fundamentally changed, Miao Wei, former head of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, said in a speech at the second plenary meeting of the fourth session of the 13th CPPCC National Committee.
Miao highlighted problems restricting the high-quality development of China’s manufacturing industry. The market-based pricing mechanism for production factors is not perfect, and the costs of energy, land and environmental protection don’t fully reflect the relationship between market supply and demand or the degree of resource scarcity. The tax burden on enterprises remains heavy, and financial support for the manufacturing sector urgently needs to be strengthened, Miao said.
“Since the China-US trade and technology conflict began, the supply chain has been disrupted, and now we need to rebuild the competitiveness of the industry and supply chains on our own,” Hong Tao, director of the Institute of Business Economics at Beijing Technology and Business University, told the Global Times, noting that the chip issue is also forcing China to make a change.
Miao said that the reason for the inadequate level of innovation in China’s manufacturing sector is the repetitive, scattered and inefficient allocation of resources, and structural defects in the supply system of key generic technologies. China also needs to speed up the development of qualified personnel to support the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry. Miao said that there is a shortage of talent in emerging industries, and the proportion of innovative and highly skilled talent is low, which has become a major constraint to the development of the manufacturing industry. This issue warrants great attention to achieve enhanced development, Miao said.
Chinese Policies Promoting its Modern Innovation Initiative
China’s modern approach to indigenizing innovation has been introduced through three landmark policies, described in detail in Part II of this analysis. The first was China’s Medium- and Long-Term Program for Science and Technology Development (MLT). Initiated in 2006, this called for domestically led innovation in 402 core technologies.
By 2015, China’s Made in China 2025 (MiC) plan placed greater emphasis on indigenizing innovation within China’s manufacturing sector. Its objective was to help transform the world’s largest manufacturing hub into one that was more globally competitive and markedly more dependent on home-grown technology by focusing on nine broad goals. In response, Chinese firms ramped up their indigenization efforts in core technologies and attempted to increase China’s domestic value-added contributions along globally integrated manufacturing supply chains.
Made in China 2025
On 12 March 2021, China released an outline of its 14th Five Year Plan (FYP) (2021–2025). The document charts a strategic, innovation-driven blueprint for Chinese development in the short- and medium-term. Science and technology and innovation in development, which were first highlighted in the 12th FYP, remain key ambitions. Innovation-driven development has become a national strategy for China, along with nurturing talent in science and education. Indeed, the second chapter in the 14th FYP describes innovation as the ‘heart’ of China’s modernisation drive. In order to fulfil China’s ambition to become a world-leading innovator by 2035, the outline elevates self-reliance and self-improvement (zili ziqiang) in science and technology as strategic action items.
It is a national strategic plan and industrial policy of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) to further develop the manufacturing sector of the People’s Republic of China, issued by Premier Li Keqiang and his cabinet in May 2015. As part of the Thirteenth and Fourteenth Five-year Plans, China aims to move away from being the “world’s factory”—a producer of cheap low-tech goods facilitated by lower labour costs and supply chain advantages. The industrial policy aims to upgrade the manufacturing capabilities of Chinese industries, growing from labor-intensive workshops into a more technology-intensive powerhouse.
The stated goals of Made in China 2025 include increasing the Chinese-domestic content of core materials to 40 percent by 2020 and 70 percent by 2025. To help achieve independence from foreign suppliers, the initiative encourages increased production in high-tech products and services, with its semiconductor industry central to the industrial plan, partly because advances in chip technology may “lead to breakthroughs in other areas of technology, handing the advantage to whoever has the best chips – an advantage that currently is out of Beijing’s reach
With the launch of its government’s Made in China 2025 (MiC 2025) plan in 2015, the quest for innovation took on an even greater salience. This initiative built upon the founding objectives of the MPL, while modernizing its focus, broadening its scope, and attaching more defined implementation plans to effectuate its policy direction.
Industries integral to MIC 2025 include aerospace, biotech, information technology, smart manufacturing, maritime engineering, advanced rail, electric vehicles, electrical equipment, new materials, biomedicine, agricultural machinery and equipment, pharmaceuticals, and robotics manufacturing, many of which have been dominated by foreign companies
It also represented China’s first focused development plan targeting manufacturing, inspired in large part by Germany’s “Industrie 4.0” initiative, and is geared towards transforming the world’s largest manufacturing hub into one that is markedly more innovative and globally competitive. MiC 2025 has set out nine broad goals, each associated with specific implementation targets. These goals include (1) improving China’s manufacturing innovation; (2) integrating information technology (IT) into manufacturing; (3) bolstering China’s industrial production; (4) fostering Chinese brands; (5) enforcing green technologies; (6) promoting breakthrough technologies in 10 key sectors; (7) restructuring manufacturing to accommodate technological change; (8) promoting service-oriented manufacturing; and (9) better integrating China’s manufacturing with global production chains.
China has also attempted to meet its objectives by sourcing the majority of robotic equipment, tools for its electric car batteries (nickel-manganese-cobalt oxide or “NMC”) and other high-tech products domestically. The MiC 2025 plan has ramped up the indigenization of core technologies while increasing China’s forward value-added contributions along global manufacturing supply chains.
Finally, China’s 13th Five-Year Science and Technology Plan (an offshoot of the broader 13th Five-Year Plan) set out ambitious implementation plans aimed at transforming China into an even more innovative economy. Chief among those were plans to ensure that, by 2020, at least 60 percent of China’s economic growth derived from productivity-enhancing scientific and technological advances enabled by significant increases in R&D expenditures, the doubling of patent applications, and other numerical targets.
14th five-year plan for 2021-25, and its vision through 2035.
In a departure from previous FYPs, the 14th iteration proposes increasing research and development (R&D) spending by at least 7 per cent every year between 2021 and 2025, and that R&D intensity — gross expenditure on R&D as a percentage of GDP — exceed levels recorded during the 13th FYP period. We will enhance the capacity of enterprises to achieve technological innovation, unlock the creativity of talent, and improve the systems and mechanisms for making scientific and technological innovation,” Li said.
Artificial intelligence and quantum information are among the seven key areas China has identified as priorities for development as it seeks to become a global leader in the scientific field by 2035. Integrated circuits, brain sciences, genetics and biotechnology, clinical medicine and health care, and deep Earth, sea, space and polar exploration were named as the other five sectors that will be given priority in terms of funding and resources, according to a draft of the government’s 14th five-year plan for 2021-25, and its vision through 2035.
The draft, which was released in March 2021 at the opening session of the National People’s Congress in Beijing, said innovation and technological self-sufficiency were at the core of China’s strategy to “develop new advantages” in the face of increased hostility and decoupling pressures from major Western countries.
The 14th FYP focusses on upgrading Chinese manufacturing and transforming China into an advanced manufacturing superpower. The plan calls for boosting global competitiveness in areas such as robotics, new energy vehicles, aerospace and agricultural machinery. To best achieve these goals, the country should adopt a more market-oriented approach and cut red tape.
Military Innovation
However China is still accused of stealing western technologies. Now china is taking large number of measures to provide thrust to innovation including boosting civil military integration, Five-year plan, National R&D plan, National Medium to Long-term Plan (MLP), and establishing Chinese DARPA.
To boost innovation, Beijing also aims to establish more national laboratories with a specific focus on AI and quantum information research. China is already conducting defence-related research on the applications of technologies such as quantum information and AI, and the 14th FYP indicates that this remains a core ambition for at least the near term. Indeed, the 14th Five-Year Plan (FYP, 2021–25) highlighted that China will focus on improving its technological strengths in key areas such as next-generation artificial intelligence, quantum information, semiconductors, deep space, deep sea and polar exploration.
Chinese President Xi Jinping has tasked the new People’s Liberation Army (PLA) Strategic Support Force (SSF) with pursuing “leapfrog development” and advancing military innovation. According to its commander, Gao Jin, the SSF will “protect the high frontiers and new frontiers of national security,” while seeking to “seize the strategic commanding heights of future military competition.” Through its integration of space, cyber, and electronic warfare capabilities, the SSF may be uniquely able to take advantage of cross-domain synergies resulting from the inherent interrelatedness and technological convergence of operations in these domains. The SSF has produced an “Innovation-Driven Development Strategy” that incorporates efforts to advance the construction of a cadre of innovative, talented personnel and to “cultivate the spirit of innovation.”
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corp., the main contractor for the Chinese space program, has teamed up with a number of state-owned enterprises to establish a RMB150 billion (US$21.78 billion) guidance fund to invest in innovative technologies. The vehicle will focus on clean energy, new energy vehicles, quantum teleportation, 3D printing, robotics, graphene, biomedicine, energy saving and environment protection sectors, with an aim to enhance the innovation capability of state-owned enterprises, assist develop emerging industries, as well as push for collaborative innovation between state-owned enterprises and other institutions.
PLA to enter second phase of reform
Draft versions of the 14th FYP published by Xinhua also provide insight into the focus areas for the PLA’s next phase of modernisation. The Chinese government had previously intended for the PLA to achieve basic mechanisation and make progress towards informatisation by 2020, but recent statements indicate that this goal has not been fully realised. Achieving full mechanisation and informatisation is thus likely to continue to be an ambition for the next few years.
Nevertheless, 2021 marks a new phase of PLA reform towards the final goal of building a world-class military by mid-century. As the draft FYP states, the PLA’s next goals are centred on army building –strengthening the army through politics, reform, science and technology, talent and rule of law – by 2027 (the centenary of the PLA’s founding), and speeding up and improving efficiency in terms of military modernisation, which it aims to achieve by 2035.
Here, the FYP provides insights into where budget spending might be allocated in the next five years. The document emphasises the modernisation of weapons and equipment, independent and original innovation in national defence science and technology, the development of strategic frontier and disruptive technologies, and accelerating upgrades of and development in intelligent weapons and equipment. But equal attention is given to the modernisation of military theory, personnel and organisation, the creation of new combat forces in new domains, and joint training. Military-civil fusion is again promoted as a way of achieving the PLA’s ambitious reform goals.
References and resources also include:
http://www.asianscientist.com/2016/04/topnews/china-five-year-plan-innovation-science-spending/
http://english.cctv.com/2016/07/05/VIDE9aDvkSenCetqjR36ZdqH160705.shtml
http://www.atimes.com/article/china-to-build-neutrino-observatory-700-meters-underground/
http://english.cas.cn/newsroom/china_research/201812/t20181210_201975.shtml
https://www.globaltimes.cn/page/202103/1217538.shtml
https://www.iiss.org/blogs/analysis/2021/03/chinas-new-five-year-plan-and-2021-budget
 International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis


