In the world of computer chips, big players like Intel and Arm have long dominated the market, licensing their proprietary designs to customers who pay a premium for customized chips. However, the rise of an open standard called RISC-V is changing the game, allowing anyone to design a chip for …
Read More »Revolutionizing Air Warfare: Exploring the Capabilities and Challenges of Autonomous Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCAs)
The current generation of aircraft faces an ever-evolving set of challenges that demand the development of next-generation aircraft. One of the most significant factors driving the need for next-gen aircraft is the rise of advanced anti-air defense systems like the S-400, which are increasingly able to detect stealthy aircraft at …
Read More »How Military or Battlefield Internet of Things(MIoT /BIoT) Will Provide Information Dominance
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers (UIDs) and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction. The number of devices that use it to …
Read More »China’s Semiconductor Industry: A Race to Catch Up with the Global Chip Making Leaders
China’s semiconductor industry is experiencing rapid development in recent years, as the country aims to become a global leader in the production of computer chips. The country has made significant investments and advancements in chip-making technology, as it seeks to catch up with other major players in the industry. …
Read More »Project Overmatch: The Future of Maritime Data Technology for the U.S. Navy
The maritime environment is vast and complex, covering over two-thirds of the Earth’s surface and presenting a range of challenges for naval forces. In addition to natural factors such as weather, ocean currents, and sea states, the maritime environment is also characterized by an increasing range of advanced naval threats …
Read More »The Future of Coding: How AI is Changing the Game
Coding is a skill that is in high demand. It is the foundation of many different industries, from software development to web design to data science. As the world becomes increasingly digital, the demand for coders is only going to grow. However, coding can be a challenging and time-consuming skill …
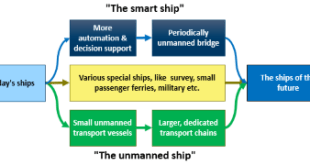
Read More »From Ships to Smart Cities at Sea: How IoT and AI are Revolutionizing the Maritime Industry”
The maritime industry is one of the oldest and most important industries in the world. It is responsible for transporting goods and people around the globe, and it plays a vital role in the global economy. However, the maritime industry is also facing a number of challenges, including rising fuel …
Read More »The Future of Aerial Combat: Exploring the Possibilities of AI-Piloted Fighter Jets
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) technology has opened up exciting possibilities for the aviation industry, particularly in the area of aerial combat. With the use of AI-piloted fighter jets, the future of aerial combat is rapidly changing, and the implications are significant. The concept of using AI to pilot …
Read More »Exploring the Future of Space-based IoT: Technologies and Trends in Space-based Internet-of-Things (IoST)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers (UIDs) and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction. The Internet of Things (IoT) is now globally …
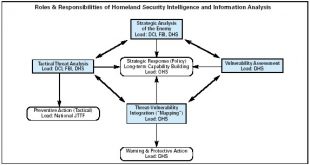
Read More »Securing our Future: The Role of Early Warning Systems and Technologies in Preventing Counterterrorism
Introduction In an ever-changing world, security concerns have become paramount, with terrorism posing a significant threat to global stability and peace. To safeguard our future, we must adopt proactive measures to prevent acts of terror rather than simply reacting to their consequences. Early warning systems and advanced technologies have emerged …
Read More » International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis