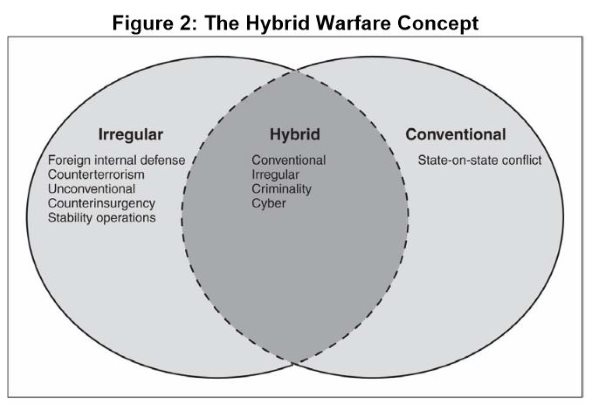
In 2050, the battlefield as we know it will be reshaped by advancements in hybrid warfare. This form of warfare, which blends conventional, irregular, and cyber warfare, will leverage a fusion of emerging technologies to redefine military strategies and warfighting capabilities. From artificial intelligence (AI) to quantum computing, and from …
Read More »Ammonia-Fueled Marine Engines: Charting a Course Toward Carbon-Neutral Shipping
The maritime industry faces unprecedented pressure to reduce its carbon footprint as global emissions regulations tighten and the demand for sustainable propulsion grows. In response, ammonia-fueled marine engines have emerged as a promising solution for achieving carbon-neutral shipping. Leveraging ammonia—a fuel with zero direct carbon emissions when produced via renewable …
Read More »New Wind Propulsion Concepts and Technologies: Enabling Wind-Assisted Commercial Ships and Tankers
The shipping industry is navigating a critical juncture in its push toward sustainability, driven by the need to cut greenhouse gas emissions and meet stringent international targets. Wind propulsion technologies such as rigid sails, rotor sails, and automated wings are helping the maritime industry take a bold step toward cleaner, more …
Read More »The Rise of Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs): Transforming Naval Warfare
Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs) are revolutionizing how we explore and protect our oceans. These autonomous vessels, operating at or near the sea surface without any onboard operators, are increasingly being employed across various sectors. From monitoring marine life to enhancing military surveillance, piracy control, and safeguarding offshore industries like gas, …
Read More »The Global Marine Battery Market: Navigating Towards a Sustainable Future
he marine industry is experiencing a transformative shift, driven by a global push towards electrification, stringent environmental regulations, and advancements in energy-efficient propulsion systems. The global marine battery market was valued at USD 1.06 billion in 2023 and is projected to experience significant growth, reaching USD 5.40 billion by 2032. …
Read More »Marine Batteries: Powering the Oceans
The marine industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the global push toward sustainability and the demand for cleaner, more efficient power sources. Central to this revolution is the development and deployment of advanced marine batteries, which are rapidly becoming the backbone of modern boating, from recreational vessels to …
Read More »DARPA’s Defense Applications of Innovative Remote Sensing (DAIRS): Innovating Remote Sensing with Surface-Wave Over-the-Horizon Radar (SWOTHR)
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Defense Sciences Office (DSO) has issued a Disruption Opportunity (DO) that invites innovative basic or applied research concepts in the field of remote sensing, with a specific focus on surface-wave over-the-horizon radar (SWOTHR) and environmental characterization. This opportunity is part of DARPA’s broader …
Read More »DARPA’s BLUE Program: Revolutionizing Ocean Energy with Marine Biomass
In a world increasingly focused on sustainable energy solutions, DARPA’s latest initiative, the BioLogical Underwater Energy (BLUE) program, is setting its sights on a groundbreaking approach to harnessing the vast, untapped energy potential of our oceans. This innovative program aims to develop power supplies that capture and convert microscopic marine …
Read More »Submarine Accidents and Incidents: Lessons from the Depths
Submarines, the silent sentinels of the seas, are marvels of modern engineering, capable of operating undetected beneath the ocean’s surface. However, these complex machines and their missions are fraught with inherent risks. Over the years, several submarine accidents and incidents have underscored the perilous nature of underwater operations. By examining …
Read More »Silent and Deadly: Navies Upgrade Submarine Electronic Warfare for the Modern Battlefield
In the shadowy depths of the world’s oceans, submarines navigate unseen, serving as silent sentinels of naval power. These underwater vessels, vital to national security and maritime dominance, are undergoing significant technological transformations. The advent of new electronic warfare (EW) technologies is revolutionizing submarine capabilities, ensuring that navies can maintain …
Read More » International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis