The airspace above future battlefields is expected to be increasingly congested with large numbers of unmanned aerial systems, manned aircraft, munitions and missiles filling the skies. The situation gets more complicated when considering that the usage of the airspace by all actors will increase significantly in the future, resulting in …
Read More »Urban Air Mobility, using eVTOL vehicles technologies taking off
The International Air Transport Association (IATA) has estimated that the number of passengers traveling by aircraft could double to 8.2 billion by 2037. According to the UN, 68% of the population is expected to live in urban areas by 2050. The growing number of vehicles in urban areas has resulted …
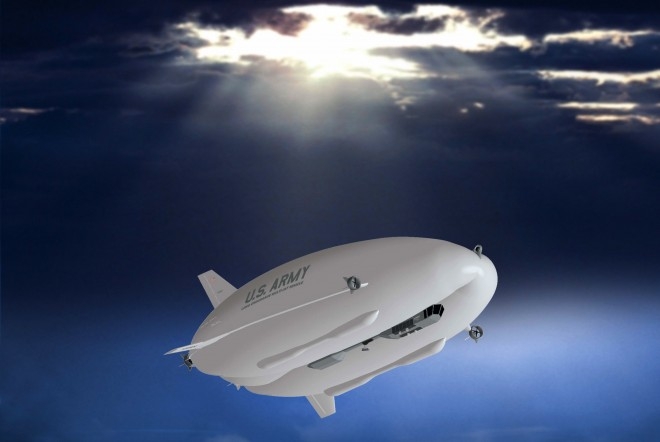
Read More »Airships return for future Aviation, Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance, and cruise missile defense.
Airship is a type of lighter-than-air aircraft which can navigate through the air under its own power. They are different from Aerostats that gain their lift from large gas bags filled with a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air. Historically, airships have been used in applications …
Read More »RTCA DO-254 Airborne Electronic Hardware Standard
The growing demand for high-efficiency fighter aircraft, commercial airbuses and the ever-evolving Aerospace and Defense requirements are driving the demand for next-gen airborne electronics systems. Air transportation agencies and aviation OEMs across the globe have been striving to build next-generation Airborne electronics systems to make flying more reliable, predictable, and …
Read More »Synthetic and Sustainable Aviation fuels (SAF)
A big push has been to increase the efficiency of aircraft engines, mainly to make them go faster, to fly higher and use less fuel. Now a new concern has come to the fore, that of environment. We have to use as little fuel as possible, create as little …
Read More »Air-launch-to-orbit brings space launch to any airport and covert military satellite launches
There are three major launch types for spacecraft: vertical takeoff, horizontal takeoff, and air launch. The cost of launching into space is often measured by the change in velocity required to reach the destination orbit, known as delta-v or Δv. The amount of Δv required for a mission depends on …
Read More »Airforce develop Artificial Intelligence and Autonomous Systems to meet challenges of Cyber-Attacks, Anti-Access/Area-Denial (A2SD) actions and Space Threats
The current Armed drones like Predators and Reapers are essentially remote controlled that is they involve human operators remotely controlling the vehicle with the assistance of fairly low levels of automation for some functions (e.g., the operator specifies waypoints to be followed by the platform). Systems like these have proved …
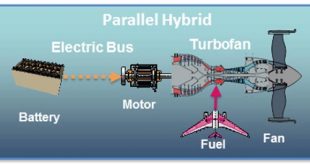
Read More »Hybrid-Electric Propulsion for Military aircraft to power radars to laser weapons payloads
The civil global aviation market has experienced considerable economic growth in recent years and will keep increasing. It is estimated that around 1300 new international airports will be required, and the commercial aircraft fleet will double by 2050, with a projected passenger throughput of 7.2 billion in 2035. This growth …
Read More »Armed Crop Dusters for Security and Military Missions
A crop duster, is usually, an aircraft used for dusting or spraying large acreages with pesticides. Aerial spraying and dusting permit prompt coverage of large areas at the moment when the application of pesticide is most effective and avoid the need for wheeled vehicles that might damage crops. Agricultural …
Read More »Military Aerospace (Aircraft ) materials trends and market growth
According to the International Air Transport Association (IATA), the demand for air travel rose by 7.4% in 2018 from 2017 levels. Air passengers accounted for 81.9% of the load factor on aircrafts, while freight load was 49.3%, the IATA data reveals. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has created turmoil in the …
Read More » International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis