In the dynamic world of engineering, the advent of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) has revolutionized how professionals approach the design, analysis, and optimization of complex systems. Gone are the days when engineers relied solely on physical prototypes and manual calculations to validate their designs. Today, CAD and CAE tools have transformed engineering analysis into a virtual simulation, allowing for greater precision, efficiency, and innovation.
The Rise of CAD and CAE
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) emerged as a powerful tool in the late 20th century, enabling engineers and designers to create detailed 2D and 3D models of products and structures. CAD software allowed for precise geometric modeling, enabling engineers to visualize and refine their designs in a digital environment. This shift from manual drafting to digital modeling marked the beginning of a new era in engineering.
In today’s world, engineering plays a part in almost everything that surrounds us, and with innovations continuously being brought to market, engineering is experiencing a steady growth extending to all of its wide-ranging facets. Computer-aided engineering (CAE) is the broad usage of computer software to aid in engineering analysis tasks. Building on the foundation laid by CAD, Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) introduced advanced analytical capabilities to the design process. CAE tools enabled engineers to simulate and analyze the behavior of their designs under various conditions, such as stress, heat, and fluid dynamics. This ability to virtually test and validate designs before physical prototyping significantly reduced development time and costs. Simply put, you can create 2D and 3D objects using CAD, while you can analyze how that object will behave using CAE tools. The automated design tools provided by CAE have transformed engineering analysis from a ‘hands-on’ experience to virtual simulation.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is a subset of CAE that focuses on the physical layout and drawing development of system designs. In industries like electronics, CAD tools—often referred to as Electronic CAD (ECAD) or Electronic Design Automation (EDA)—are essential for creating detailed 3D models. These models enable engineers and designers to share, review, simulate, and modify designs with ease, fostering innovation and accelerating the time-to-market for new products.
In the aerospace industry, CAD is indispensable. Three-dimensional models allow engineers to identify potential flaws and optimize designs before a single prototype is built. This not only saves resources but also enhances safety by preventing costly and potentially dangerous errors during the production phase. CAD platforms enable the creation of intricate 2D and 3D objects using tools like extrude, cut, and revolve, with the added benefit of parametric design capabilities that allow for easy adjustments based on specific requirements.
Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE)
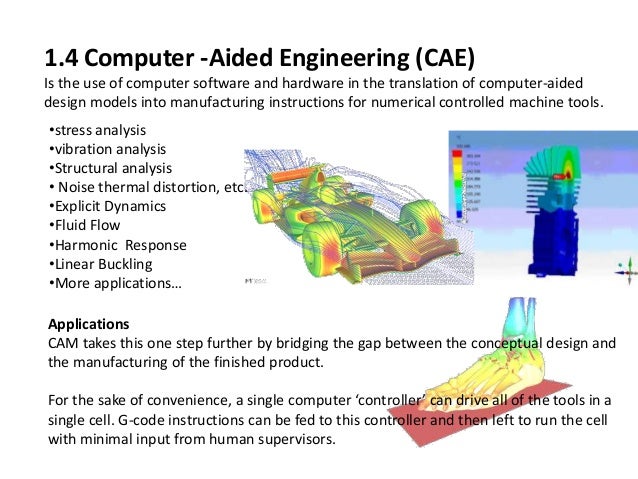
While CAD is primarily concerned with the creation of models, CAE takes the process a step further by enabling detailed engineering analysis. Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) refers to the use of computer software to assist in engineering analysis tasks, improving product designs and resolving engineering challenges across various industries. CAE encompasses a wide range of activities, including the simulation, validation, and optimization of products, processes, and manufacturing tools. CAE tools allow for the examination of fluid dynamics, kinematics, stress analysis, and more, providing insights that are critical for product development. By leveraging advanced software, engineers can analyze complex systems and predict how they will perform under different conditions, significantly enhancing the design process.
CAE software not only includes CAD but also incorporates Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM), Finite Element Analysis (FEA), Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), and other advanced techniques. These tools have revolutionized engineering by transforming it from a hands-on experience into a sophisticated process of virtual simulation.
Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a powerful numerical technique used to simulate physical phenomena. Engineers use FEA software to minimize the need for physical prototypes, optimizing designs in the early stages of development.
It is necessary to use mathematics to comprehensively understand and quantify any physical phenomena such as structural or fluid behavior, thermal transport, wave propagation, the growth of biological cells, etc. Differential equations not only describe natural phenomena but also physical phenomena encountered in engineering mechanics. These partial differential equations (PDEs) are complicated equations that need to be solved in order to compute relevant quantities of a structure (like stresses (ϵ), strains (ϵ), etc.) in order to estimate the structural behavior under a given load.
FEA method involves solving complex partial differential equations (PDEs) that describe natural and engineered processes. By breaking down a structure into millions of small elements, FEA provides an approximate solution that is both detailed and highly accurate. It is important to know that FEA only gives an approximate solution to the problem and is a numerical approach to get the real result of these partial differential equations. To be able to make simulations, a mesh, consisting of up to millions of small elements that together form the shape of the structure, needs to be created. Calculations are made for every single element. Combining the individual results gives us the final result of the structure. The results of a simulation based on the FEA method are usually depicted via a color scale that shows, for example, the pressure distribution over the object., which help engineers understand how different parts of a structure will behave under various conditions.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is another crucial aspect of CAE, involving the mathematical modeling and numerical analysis of fluid flow. CFD software allows engineers to examine how fluids behave under various conditions, taking into account properties such as velocity, pressure, temperature, and viscosity. To virtually generate an accurate solution for a physical phenomenon associated with fluid flow, those properties have to be considered simultaneously.
By solving the Navier-Stokes equations—complex PDEs that describe fluid flow—engineers can create accurate simulations that are essential for applications ranging from aerospace to data center cooling. The verification of the mathematical model is extremely important to create an accurate case for solving the problem.
Multibody Dynamics (MBD)
A multibody dynamic (MBD) system is one that consists of solid bodies, or links, that are connected to each other by joints that restrict their relative motion. Multibody Dynamics (MBD) focuses on the analysis of systems composed of multiple interconnected solid bodies. The study of MBD is the analysis of how mechanism systems move under the influence of forces, also known as forward dynamics. A study of the inverse problem, i.e. what forces are necessary to make the mechanical system move in a specific manner is known as inverse dynamics. Motion analysis is important because product design frequently requires an understanding of how multiple moving parts interact with each other and their environment.
From automobiles and aircraft to washing machines and assembly lines – moving parts generate loads that are often difficult to predict. Complex mechanical assemblies present design challenges that require a dynamic system-level analysis to be met. Motion analysis enables one to meet these challenges by quickly evaluating and improving designs for important characteristics like performance, safety and comfort. MBD tools enable engineers to simulate and analyze these interactions, improving the design and performance of complex mechanical assemblies.
The CAE Process
The CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) process is a comprehensive approach that consists of three critical stages: preprocessing, solving, and postprocessing.
- Preprocessing: The journey begins with the preprocessing phase, where engineers meticulously build a virtual representation of the design. This involves modeling the geometry, defining the material properties, and applying loads and boundary conditions that mimic real-world scenarios. The accuracy of this phase is paramount, as it lays the foundation for the entire simulation. Engineers must consider various factors such as stress, temperature, fluid flow, and electromagnetic fields, depending on the nature of the analysis. The preprocessing stage transforms a conceptual design into a detailed, analyzable model ready for simulation.
- Solving: Once the model is fully defined, the next step is solving. During this phase, advanced computational algorithms take over, applying mathematical formulations to simulate the physical behavior of the design under the specified conditions. The solver processes vast amounts of data, performing calculations that capture the complex interactions within the system. Depending on the complexity of the model and the type of analysis being performed—be it structural, thermal, or fluid dynamics—this step can be computationally intensive. The result is a detailed prediction of how the design will perform in the real world, revealing potential issues that might not be apparent through traditional testing methods.
- Postprocessing: After the solver has completed its work, the final phase is postprocessing. Here, the raw data from the solver is transformed into interpretable results through visualizations such as graphs, contour plots, and animations. Engineers can analyze these results to assess the performance of the design, identify areas of concern, and explore alternative solutions. Postprocessing is crucial for making informed decisions; it allows engineers to evaluate the safety, efficiency, and feasibility of the design before moving forward to production. The insights gained during this phase can lead to design refinements, optimization, and ultimately, the successful realization of the product.
By following this structured approach, the CAE process ensures that engineering designs are thoroughly tested and validated in a virtual environment, reducing the need for physical prototypes and accelerating the development cycle.
Benefits of CAE Tools
CAE tools offer numerous benefits, particularly in terms of cost reduction, efficiency, and accuracy. By enabling virtual simulations, CAE reduces the need for physical prototypes, saving both time and money. It also minimizes errors in the design process and allows for the thorough analysis of components and assemblies. As a result, CAE tools are widely used across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and shipbuilding, where precision and reliability are paramount.
The integration of CAD and CAE has fundamentally changed how engineers approach the design and analysis process. Virtual simulation has become the cornerstone of modern engineering, offering numerous benefits over traditional methods:
- Enhanced Precision and Accuracy: Virtual simulations allow engineers to create highly detailed models that accurately represent the real-world behavior of a product or system. By simulating different scenarios, engineers can identify potential issues and optimize designs before they reach the physical testing stage.
- Reduced Time and Costs: Traditional engineering analysis often required the creation of multiple physical prototypes, each iteration involving significant time and resources. CAD and CAE tools enable engineers to test and refine their designs in a virtual environment, reducing the need for costly prototypes and shortening the development cycle.
- Improved Innovation and Creativity: With the ability to rapidly iterate and explore different design possibilities, engineers can push the boundaries of innovation. Virtual simulation allows for the exploration of unconventional designs that might have been too risky or expensive to prototype physically.
- Risk Mitigation: Virtual simulations provide engineers with the ability to test their designs under a wide range of conditions, including extreme environments that would be difficult or dangerous to replicate physically. This helps in identifying potential failure points and mitigating risks early in the development process.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact: By reducing the need for physical prototypes and minimizing material waste, virtual simulation contributes to more sustainable engineering practices. Engineers can also use simulations to optimize designs for energy efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of their products.
Applications Across Industries
The impact of CAD and CAE on virtual simulation extends across various industries, from automotive and aerospace to civil engineering and consumer electronics. For example:
- Automotive Industry: Virtual simulations are used to optimize vehicle designs for safety, performance, and fuel efficiency. Engineers can simulate crash tests, aerodynamic flow, and thermal management, ensuring that the final product meets the highest standards.
- Aerospace Industry: In aerospace, virtual simulations are critical for analyzing the structural integrity of aircraft, optimizing aerodynamics, and ensuring compliance with stringent safety regulations. Engineers can simulate the effects of high-altitude conditions, extreme temperatures, and aerodynamic forces on aircraft designs.
- Civil Engineering: CAD and CAE tools are used in civil engineering to simulate the behavior of structures under various loads and environmental conditions. Engineers can optimize the design of bridges, buildings, and infrastructure to ensure safety, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Consumer Electronics: Virtual simulations help engineers design and optimize electronic devices for thermal management, electromagnetic compatibility, and structural integrity. This ensures that products are not only functional but also reliable and durable.
CAE in the Space Industry
The space industry has been a pioneer in the application of CAE, with companies like MSC Software leading the way. The core of MSC Nastran, a CAE tool, was originally developed by NASA for the Apollo Space Program. Since then, CAE has played a crucial role in the development of spacecraft, enabling engineers to conduct detailed structural analyses and optimize designs for the extreme conditions of space. From multi-body dynamics to acoustics, FEA to CFD, and materials analysis, MSC Software has provided the necessary tools for engineers to tackle complex challenges.
MSC Software’s tools and solutions have been instrumental in advancing space industry simulations and related equipment design. From multi-body dynamics to acoustics, FEA to CFD, and materials analysis, MSC Software has provided the necessary tools for engineers to tackle complex challenges.
In the past decade, researchers have extensively used MSC Software to analyze various aspects of space exploration:
- Lunar Lander Dynamics: Russian researchers at RSC Energia used MSC Nastran to study the dynamics of lunar landers and ascent vehicles.
- Robotic Lander Design: Researchers at Harbin University in China coupled MSC’s Adams multi-body dynamics solver with EDEM to model a spider-like robotic lander capable of navigating rough terrain.
- CubeSat Satellite Design: A Masters Thesis from MIT investigated the stress on solar panels and hinges in a CubeSat satellite design using SimXpert and MSC Nastran.
The commercial space industry has witnessed significant growth in recent years, with companies exploring opportunities for lunar mining, asteroid exploration, and even Mars colonization. CAE tools are essential for designing and analyzing the equipment and infrastructure required for these ambitious projects.
Digital Engineering and the Department of Defense (DoD)
The Department of Defense (DoD) is increasingly adopting Digital Engineering (DE), also known as model-based engineering or model-based systems engineering, to streamline defense programs. DE initiatives, championed by the Office of the Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense for Systems Engineering (ODASD(SE)), aim to enhance efficiency and coherence in defense programs by ensuring stakeholders have access to accurate, relevant, and consistent information throughout a program’s lifecycle.
DE involves the use of digital computing, analytical capabilities, and new technologies to conduct engineering in integrated virtual environments. This approach not only improves customer and vendor engagement but also reduces response times to threats, lowers documentation costs, and enhances sustainment affordability. By enabling virtual prototyping and testing, DE reduces the need for expensive physical mock-ups and accelerates the design process.
The Rise of Cloud-Based CAE
While traditional CAD and CAE software remain powerful, they are often limited by their on-premises nature, which can be costly and difficult to use. In response, many companies are now offering cloud-based CAE solutions that enhance collaboration and accessibility. These tools allow global teams to work together seamlessly, regardless of location, and provide features that support real-time feedback and teamwork. Leading companies such as AutoDesk®, Dassault Systèmes®, Siemens®, Onshape, and SimScale have introduced cloud-based platforms that make it easier than ever to share and collaborate on complex engineering projects.
A Comparison of Popular CAD and CAE Tools and Applications
In the modern engineering landscape, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) tools are indispensable. They streamline design processes, enhance product development, and optimize engineering analysis. This article compares some of the most popular CAD and CAE tools, highlighting their applications, strengths, and unique features.
1. AutoCAD
Overview:
AutoCAD, developed by Autodesk, is one of the most widely used CAD tools in the industry. It is known for its versatility in creating detailed 2D and 3D designs.
Key Features:
- 2D and 3D Drafting: Offers robust tools for creating detailed drawings and models.
- Customizability: Users can create custom commands and automate repetitive tasks.
- Interoperability: Supports a wide range of file formats for importing and exporting data.
Applications:
AutoCAD is used across various industries, including architecture, engineering, and construction, for drafting architectural plans, engineering designs, and product designs.
Strengths:
- Extensive library of design tools.
- Strong user community and extensive online resources.
- High level of customization.
Limitations:
- Steeper learning curve for new users.
- Costly licensing.
2. SolidWorks
Overview:
SolidWorks, developed by Dassault Systèmes, is a leading CAD software known for its powerful 3D modeling capabilities and integration with CAE tools.
Key Features:
- Parametric Design: Allows users to define and modify design parameters easily.
- Assemblies: Facilitates complex assembly modeling with motion analysis.
- Simulation Integration: Built-in CAE tools for simulation and analysis.
Applications:
SolidWorks is widely used in mechanical engineering, product design, and manufacturing for creating complex 3D models and performing simulations.
Strengths:
- Intuitive user interface.
- Comprehensive simulation capabilities.
- Strong community support and resources.
Limitations:
- Can be resource-intensive.
- Expensive licensing and add-on modules.
3. CATIA
Overview:
CATIA, another product from Dassault Systèmes, is a high-end CAD tool designed for complex and large-scale design projects.
Key Features:
- Integrated Design: Combines CAD, CAM, and CAE functionalities in one platform.
- Advanced Surface Modeling: Provides tools for designing complex surfaces.
- Collaborative Design: Supports multi-disciplinary collaboration.
Applications:
CATIA is used in aerospace, automotive, and industrial design for managing complex product development processes and integrated engineering tasks.
Strengths:
- Powerful for complex designs and simulations.
- Advanced features for surface modeling and assemblies.
- Excellent for collaborative and multi-discipline projects.
Limitations:
- High cost and steep learning curve.
- May be overkill for simpler projects.
4. ANSYS
Overview:
ANSYS is a leading CAE tool known for its advanced simulation capabilities in various fields, including structural, thermal, and fluid dynamics.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Simulation: Includes modules for FEA, CFD, and electromagnetic analysis.
- High Accuracy: Provides detailed and accurate simulation results.
- Integration: Compatible with various CAD tools for seamless data transfer.
Applications:
ANSYS is used for advanced simulations in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics to predict product behavior under real-world conditions.
Strengths:
- High accuracy and detailed analysis.
- Extensive range of simulation capabilities.
- Strong integration with other tools.
Limitations:
- Expensive licensing.
- Requires significant computational resources.
5. COMSOL Multiphysics
Overview:
COMSOL Multiphysics is known for its versatility in multi-physics simulations and its integration with CAD tools.
Key Features:
- Multi-Physics Modeling: Supports coupled simulations involving multiple physical phenomena.
- Customizable Interfaces: Allows users to create custom simulation applications.
- Integration: Compatible with various CAD tools and data formats.
Applications:
COMSOL is used in research and industry for simulating complex physical interactions, including heat transfer, fluid dynamics, and structural mechanics.
Strengths:
- Versatility in multi-physics simulations.
- High level of customization and flexibility.
- Strong integration with CAD tools.
Limitations:
- High cost.
- Complexity can be overwhelming for new users.
6. Onshape
Overview:
Onshape is a cloud-based CAD tool that enables real-time collaboration and integration with various CAE tools.
Key Features:
- Cloud-Based Collaboration: Allows multiple users to work on the same design simultaneously.
- Version Control: Provides built-in version control and data management.
- Integration: Supports integration with various CAE tools and plugins.
Applications:
Onshape is used for collaborative product design and engineering, particularly in industries where real-time teamwork and cloud access are crucial.
Strengths:
- Real-time collaboration and cloud-based access.
- Integrated version control and data management.
- Flexibility and accessibility.
Limitations:
- May require a stable internet connection.
- Limited compared to some traditional CAD tools in terms of advanced features.
Both CAD and CAE tools offer unique features and strengths tailored to different engineering needs. CAD tools like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and CATIA focus on design and modeling, while CAE tools like ANSYS and COMSOL excel in advanced simulations and analysis. Cloud-based solutions like Onshape are changing the landscape by providing enhanced collaboration capabilities. Choosing the right tool depends on the specific requirements of the project, the complexity of the design, and the need for simulation and analysis.
The Future of Virtual Simulation in Engineering
As CAD and CAE technologies continue to evolve, the capabilities of virtual simulation will only expand. Advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing are poised to enhance the accuracy and speed of simulations, making them even more integral to the engineering process. Additionally, the integration of virtual and augmented reality could enable engineers to interact with their designs in entirely new ways, further blurring the line between the digital and physical worlds.
The global market for Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by advancements in Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD). As companies continue to leverage cloud computing, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, CAE tools will become even more powerful and accessible. Emerging technologies like building information modeling, concurrent engineering, and 3D printing are also expected to influence the CAE market, further expanding its reach and impact.
In conclusion, the transformation of engineering analysis through CAD and CAE into virtual simulation has ushered in a new era of precision, efficiency, and innovation. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly play an even more significant role in shaping the future of engineering across industries.
References and Resources also include:
https://www.mscsoftware.com/sites/default/files/space-cae-the-first-and-final-frontier.pdf
https://learnmech.com/cae-introduction-computer-aided-engineering/
 International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
