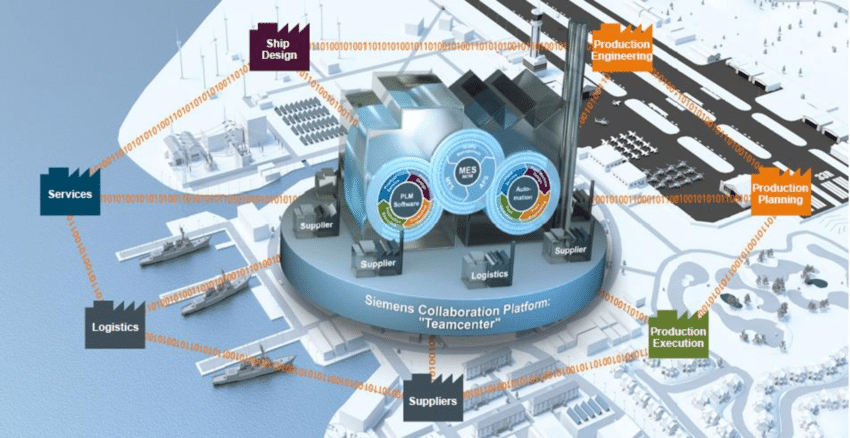
Introduction to Industry 4.0 in Shipbuilding In the ever-evolving realm of shipbuilding, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies marks a pivotal turning point. Industry 4.0, characterized by interconnected digital systems and smart manufacturing processes, is reshaping shipyards worldwide. From enhancing productivity to enabling customized solutions, these cutting-edge technologies are revolutionizing traditional shipbuilding practices. Join us…