Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronic systems, playing a crucial role in everything from consumer electronics to industrial machines. However, the stakes are significantly higher when it comes to aerospace and military applications. These fields demand PCBs that not only function flawlessly under extreme conditions but …
Read More »Navigating the World of Power Conversion: From SMPS to Space-Level DC-DC Converters
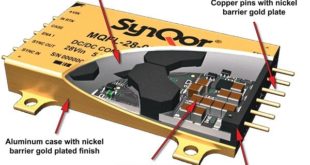
Introduction: In the landscape of electronics, the efficient conversion of power is paramount. Whether it’s for everyday consumer gadgets or critical military and aerospace applications, the ability to convert direct current (DC) from one voltage level to another is a fundamental requirement. Power conversion plays a critical role in ensuring efficiency, …
Read More »Unraveling the Complexity of Device Drivers: Kernel & User Drivers, Block Drivers, Character Drivers, and Software Drivers
In the realm of computing, device drivers serve as the crucial link between hardware components and the operating system. They enable seamless communication, ensuring that software can interact with various hardware peripherals effectively. Device drivers come in different types, each tailored to specific hardware functionalities and system requirements. In this …
Read More »DARPA SOAP Seeks Innovation: Scalable On-Array Processing to Revolutionize Signal Processing
The U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), renowned for fostering groundbreaking technologies, has issued a new challenge: the Scalable On-Array Processing (SOAP) program. This initiative aims to revolutionize the way we handle digital signal processing, particularly for large-scale applications like phased arrays. The Challenge: Breaking Through Processing Barriers Digital …
Read More »Driving Forces and Future Frontiers: Navigating the Global Military Vetronics Market
The global military vetronics market is experiencing a surge, projected to reach USD 8.14 billion by 2032. This growth is fueled by a confluence of factors, from rising geopolitical tensions to technological advancements that are transforming the battlefield. What are Vetronics? Vetronics, an abbreviation for “vehicle electronics,” serves as the …
Read More »Exploring the Power and Versatility of Embedded Linux
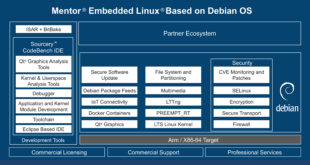
Introduction: Embedded systems have become ubiquitous in our daily lives, powering everything from smartphones and smart TVs to industrial machinery and automotive electronics. At the heart of many of these systems lies Embedded Linux, a powerful and versatile operating system that has revolutionized the way we approach embedded computing. In …
Read More »Building Better Together: How Hardware-Software Co-Design Optimizes Embedded Systems
In the realm of electronic embedded systems, where performance, efficiency, and reliability are paramount, the concept of Hardware-Software Co-Design (HSCD) has emerged as a powerful methodology for achieving optimal system-level performance. By seamlessly integrating hardware and software components at the design stage, HSCD enables developers to harness the full potential …
Read More »Tiny Targets, Big Cyber Risks: Securing Embedded Systems in a Hostile World
Embedded systems, the silent heroes of modern technology, quietly perform dedicated functions within larger systems, seamlessly integrating into our daily lives. These systems, a blend of hardware and software, cater to diverse needs, from powering smart appliances to steering critical infrastructure. However, with connectivity comes vulnerability, and embedded systems are …
Read More »Mastering the Skies: Real-Time Embedded Systems (RTES) in Aerospace and Defense
In the ever-evolving landscape of aerospace and defense, real-time embedded systems play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety, efficiency, and reliability of critical operations. From aircraft navigation to missile guidance systems, these sophisticated technologies are the backbone of modern aerospace and defense infrastructure. In this article, we’ll delve into …
Read More »Addressing the Growing E-Waste Crisis: Recycling Technologies and the Move to Biodegradable Electronics
Introduction Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has revolutionized our world, enabling the transition to an information-based society by overcoming barriers of time, distance, and human limitations in processing information. However, the rapid proliferation of electronic devices has led to a significant environmental challenge: electronic waste, or e-waste. With millions of …
Read More » International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis