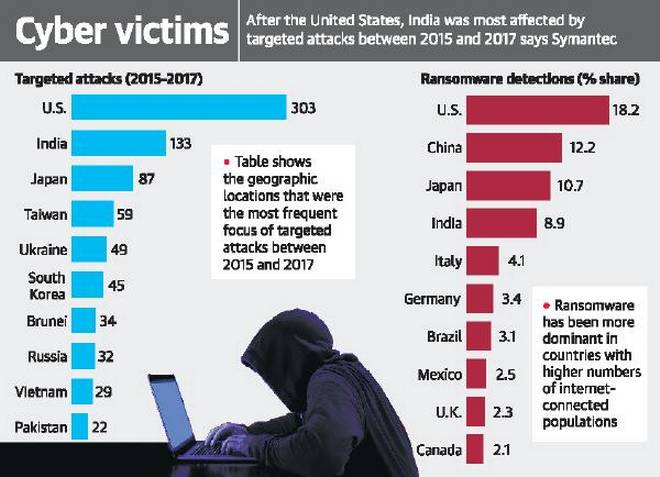
In recent years, India has faced an escalating barrage of cyber attacks originating primarily from neighboring countries like Pakistan and China. These attacks, often aimed at disrupting critical infrastructure, stealing sensitive data, or spreading misinformation, have underscored the urgent need for a comprehensive cyber security strategy. In response to these challenges, India has launched a…