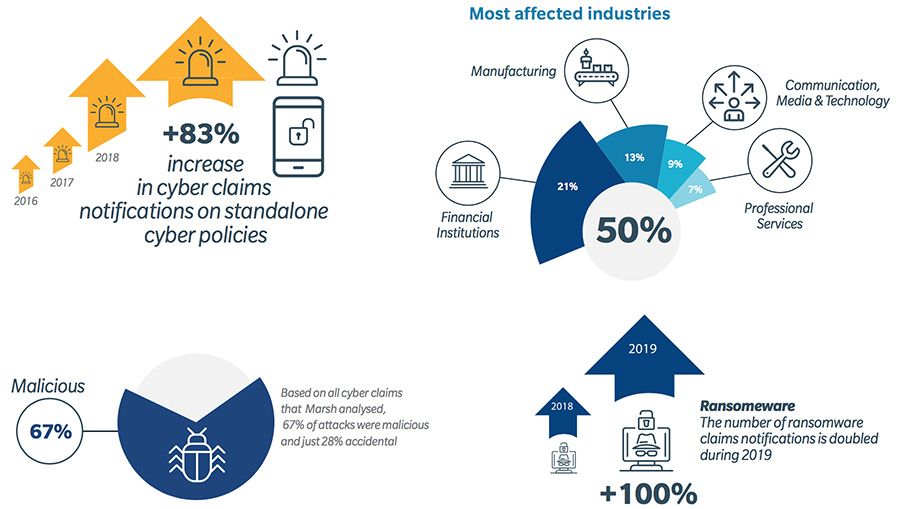
Cyber insurance is no longer optional—it’s the critical shield protecting businesses from billion-dollar cyberattacks, ransomware, and regulatory risks. Introduction In an age where digital transformation drives every sector—from healthcare and finance to manufacturing and logistics—our dependence on information technology has never been greater. While this technological evolution unlocks unprecedented levels of productivity and connectivity, it…