The recent presolicitation by the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) for the High Power Electromagnetic Systems Development, Application, and Test (HPEM DAT) project has sent ripples through the world of electronic warfare. Let’s delve into the nitty-gritty of the technological advancements this project seeks to explore. The Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) …
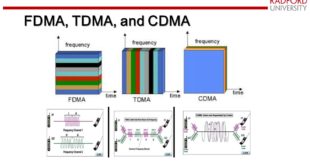
Read More »Satellite Multiple Access Techniques: TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, and Emerging Schemes
Satellites play a crucial role in global communications, enabling connectivity across vast distances where terrestrial networks are impractical. To maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of satellite communications, various multiple access techniques are employed. These techniques allow multiple users to share the satellite’s communication resources. This article explores Time Division Multiple …
Read More »Countries Advancing Satellite ELINT / COMINT constellations for countering adversary’s Military Radars and communications
In the ever-evolving arena of modern warfare, electronic intelligence (ELINT) and communications intelligence (COMINT) play critical roles. These disciplines focus on intercepting and analyzing radar and communication signals to gather valuable intelligence, jam enemy systems, and protect one’s own assets. As nations strive for technological superiority, several countries are advancing …
Read More »Exploring VxWorks: A Comprehensive Guide to Real-Time Operating Systems
Introduction: In the realm of embedded systems, real-time operating systems (RTOS) play a crucial role in ensuring deterministic behavior, reliability, and performance. Among the array of RTOS options available, VxWorks stands out as a leading choice, renowned for its robustness, real-time capabilities, and versatility across various industries. In this comprehensive …
Read More »Printed Circuit Board Market Booming: Demand Driven by Innovation and Connectivity
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the interconnection of increasingly complex electronic systems is leading to intricate designs and components. As electronic systems become more complex, so do their designs and components. Integrated electronics, such as systems-on-a-chip and multichip modules, have significantly boosted speed and reduced latency, resulting in diverse …
Read More »The Future of Electronics: Exploring Emerging Ultrawide Bandgap Materials
Introduction As we venture deeper into the realm of electronics, the quest for materials that can push the boundaries of performance and efficiency intensifies. Emerging ultrawide bandgap (UWBG) materials like cubic boron nitride (c-BN), gallium oxide (Ga2O3), and silicon nitride (Si3N4) have risen to the forefront, promising to redefine the …
Read More »Advancing Stealth: Chinese Scientists Develop Meta-Materials-Based Radar Cloaks
Stealth technology has long been a cornerstone of military innovation, offering the promise of enhanced survivability for aircraft, warships, and other assets by reducing their detectability. Traditional approaches to stealth have focused on reducing various signatures, including radar cross-sections (RCS), infrared (IR), and visual signatures. However, recent advancements in metamaterials …
Read More »The Military Antenna Market: Powering Communication, Radars and EW on the Battlefield
Introduction: In an era defined by rapid technological advancements and evolving security threats, military organizations worldwide are continually seeking innovative solutions to enhance their communication capabilities. At the heart of this quest lies the military antenna market—a dynamic sector driven by the imperative of maintaining robust and reliable communication networks …
Read More »Satellite Antenna Control Systems: Optimizing Tracking for Reliable Communication
In our interconnected world, satellite communications are crucial for various applications, including global navigation, weather forecasting, internet connectivity, and defense operations. The backbone of these communications is the satellite antenna control system, which ensures precise tracking and robust signal transmission between ground stations and satellites. Unlike fixed terrestrial communication towers, …
Read More »Navigating the Cosmos: The Intricacies of Small Spacecraft Avionics
Introduction: In the vast expanse of space exploration, the emergence of small spacecraft has revolutionized our approach to exploring the cosmos. These diminutive yet powerful vehicles, often referred to as CubeSats or nanosatellites, have opened new frontiers for scientific research, commercial endeavors, and educational initiatives. At the heart of these …
Read More » International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis