As technology continues to advance, security measures have also evolved to keep pace. One of the latest innovations in the field of security is mobile, fully autonomous security robots that are now being deployed in malls, parking lots, and neighborhood parks to enhance public safety. Autonomous security robots are an …
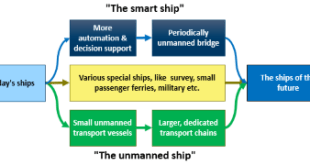
Read More »From Ships to Smart Cities at Sea: How IoT and AI are Revolutionizing the Maritime Industry”
The maritime industry is one of the oldest and most important industries in the world. It is responsible for transporting goods and people around the globe, and it plays a vital role in the global economy. However, the maritime industry is also facing a number of challenges, including rising fuel …
Read More »Closing the Gap: How the US Military’s Next-Generation Electronic Warfare Systems Are Reducing Russia’s Military Edge
All modern forces depend on unimpeded access to, and use of, the EM spectrum in conducting military operations. Therefore, there is a requirement to gain and maintain an advantage in the electromagnetic spectrum by countering adversary’s systems and protecting one’s own systems. Adversary can disrupt and degrade the navigation systems …
Read More »Modular Platforms for Multi Naval Missions: Improving Mission Effectiveness Through Flexibility and Versatility
The naval landscape is constantly evolving, and the threats facing navies around the world are becoming increasingly complex. In order to meet these challenges, navies need to be able to adapt quickly and effectively. One way to do this is to adopt modular platforms that can be configured for a …
Read More »Advanced Materials and Technologies Transforming Submarine Hulls for Enhanced Warfighting Capabilities
The world’s oceans are vast and deep, and submarines have been a vital component of naval forces for decades. These underwater vessels can operate silently, dive to great depths, and strike from unexpected directions, making them an incredibly effective tool in modern warfare. However, the ability of submarines to remain …
Read More »The Future of Aerial Combat: Exploring the Possibilities of AI-Piloted Fighter Jets
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) technology has opened up exciting possibilities for the aviation industry, particularly in the area of aerial combat. With the use of AI-piloted fighter jets, the future of aerial combat is rapidly changing, and the implications are significant. The concept of using AI to pilot …
Read More »Advanced Missile Technology: US Air Force Tests Mutant Missiles with Enhanced Agility to Strike Highly Maneuverable Aerial Targets
Missiles are guided weapons designed to deliver a destructive payload to a target. They can be launched from various platforms, including aircraft, ships, and ground-based launchers. Some missiles are designed to hit stationary targets, while others are intended to engage moving targets, such as aircraft or cruise missiles. One …
Read More »Revolutionizing Military Operations with Soldier Body Networks: Seamless Data Transmission and Enhanced Situational Awareness
The modern battlefield is constantly evolving, with new threats and challenges emerging all the time. To stay ahead of the curve, military organizations around the world are turning to advanced technologies like soldier body networks to enhance communication and situational awareness on the battlefield. These networks provide soldiers with real-time …
Read More »The Growing Threat of Smartphone Security to National Security
Smartphones are ubiquitous in modern society, and their use has become increasingly prevalent in government agencies and other sensitive settings. However, this increasing reliance on mobile technology has also raised significant concerns regarding national security. Research indicates that smartphones pose a significant security threat to government agencies and other organizations …
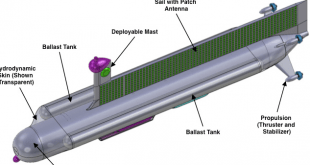
Read More »DARPA’s Arcadia Program: Using Microorganisms to Combat Asset Degradation from Marine Biofouling
UUVs are increasingly being used for a wide range of applications, from underwater exploration and surveillance to mine detection and mapping of the ocean floor. These vehicles are typically designed to operate autonomously, without human intervention, and can be deployed for extended periods of time. However, UUVs can face significant …
Read More » International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis