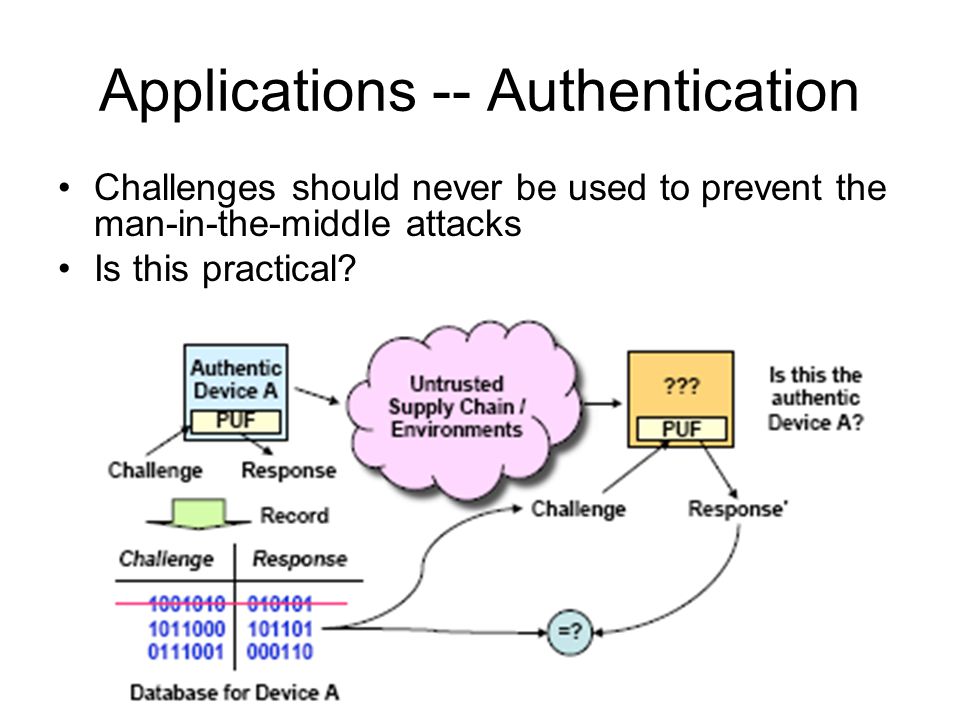
We live in digitised, connected societies, in an Internet of Things (IoT) world where our reliance on software, hardware, and the networks that connect us, grows exponentially. Our increasing global reliance on what we hope and assume are secure networks, is profound. The threat of large-scale cyber-attack has become a strategic priority for all governments…