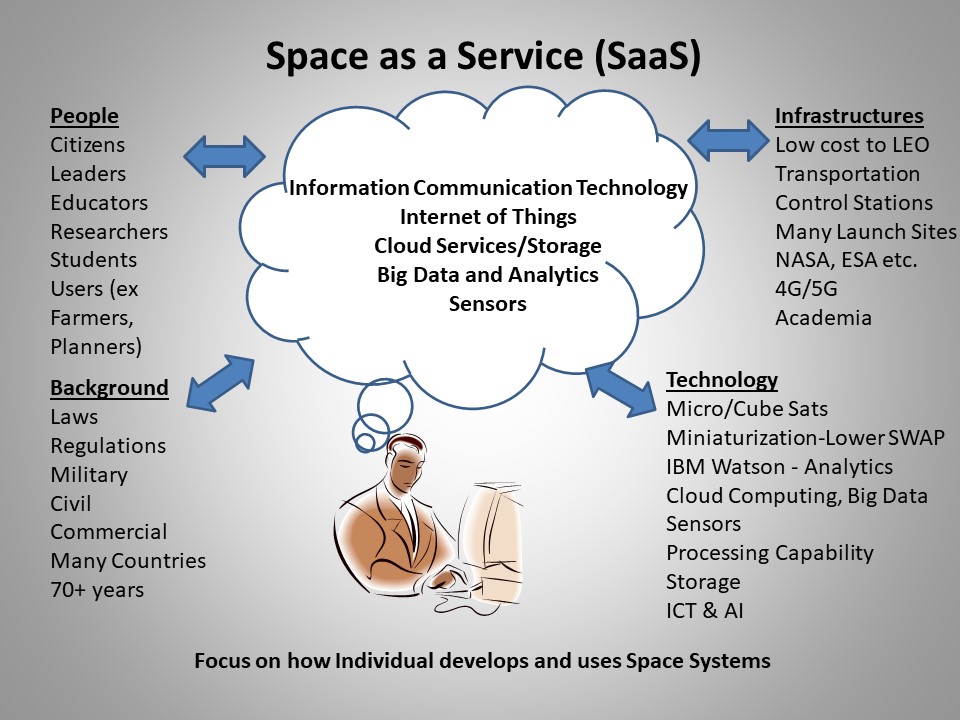
The modern space industry is witnessing exponential growth in small satellite and nanosatellite areas. Nanosatellite and microsatellite refer to miniaturized satellites in terms of size and weight, in the range of 1-10 Kg and 10-100 kg, respectively. ‘CubeSat’ is one of the most popular types of miniaturized satellites. These are the fastest-growing segments in the…