Digital battlefields, hybrid warfare, and the future of threat intelligence
IDST Intelligence Briefings
(Latest Security & Cyber Videos)
Why This Magazine Exists
Security, Cyber & Counter-Threats examines the evolving landscape of modern security in an era defined by digital conflict, hybrid warfare, and persistent global threats.
From cyber operations, information warfare, and intelligence-driven defense to counter-terrorism, internal security, and emerging threat vectors, this magazine provides strategic analysis, technical insight, and policy-relevant perspectives for decision-makers, practitioners, and researchers navigating an increasingly contested security environment.
What We Track
- Cyber warfare & cyber defense
- Information operations & influence campaigns
- National security threat assessments
- Emerging digital and hybrid warfare doctrines
- Critical infrastructure & cyber resilience
Latest Analysis & Intelligence
-

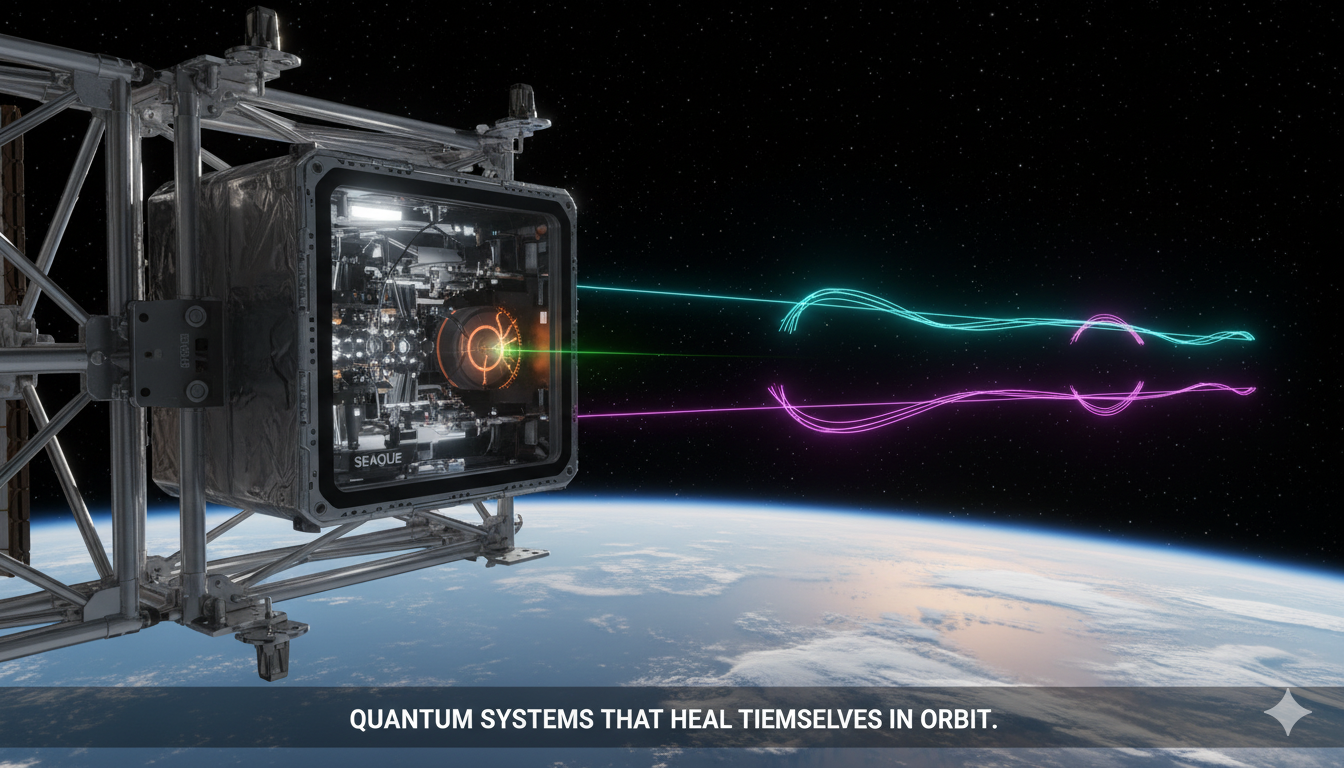
SEAQUE: Pioneering Self-Healing Quantum Technology for the Final Frontier
How NASA’s autonomous quantum experiment is shaping the future of secure communications and resilient space infrastructure. In the harsh, radiation-filled environment of space, NASA’s Space Entanglement and Annealing Quantum Experiment (SEAQUE) is quietly redefining the future of quantum technology. Deployed aboard the International Space Station, SEAQUE demonstrates that quantum systems can not only survive orbital…
-

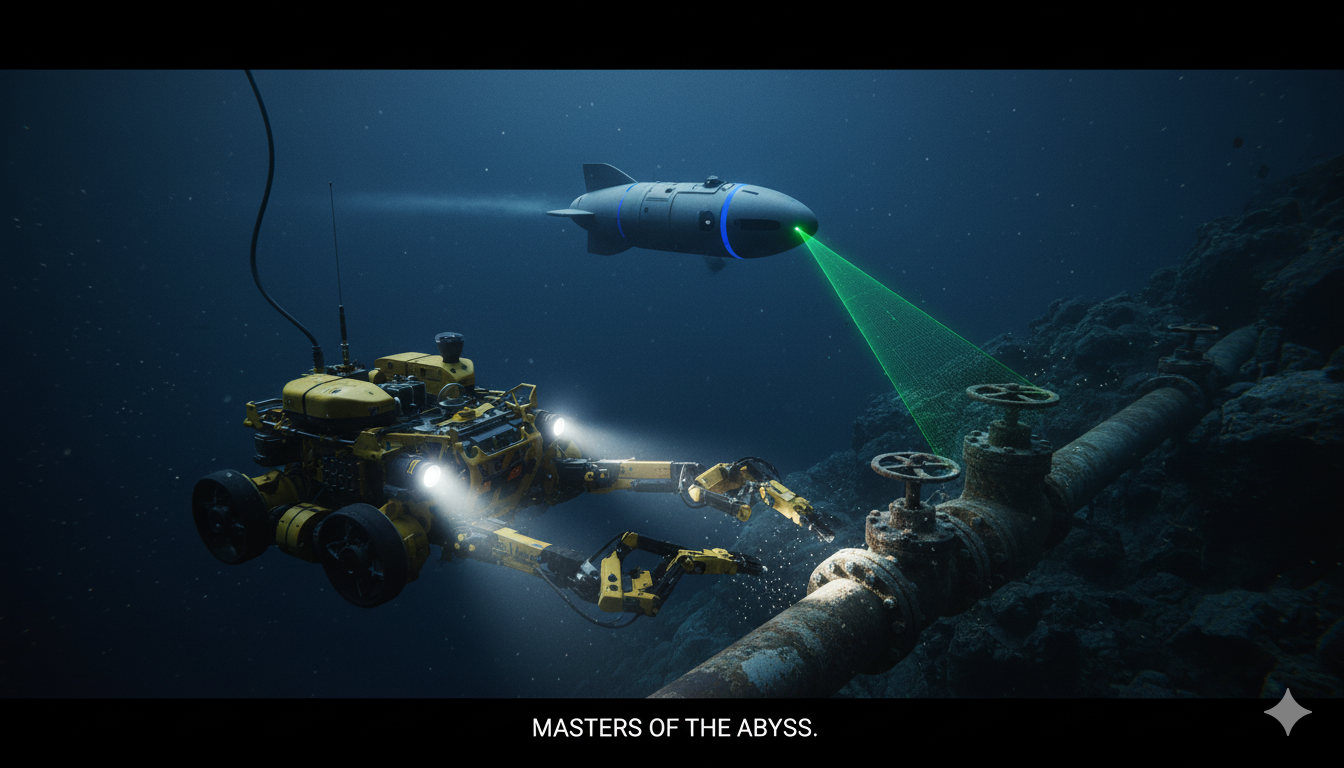
Navigating the Depths: The $4.1 Billion Offshore AUV and ROV Market Set for Robust Growth
Introduction: Exploring the Hidden Frontiers Beneath the Waves Beneath the ocean’s surface lies a vast and largely unexplored frontier — one that holds vital resources, energy potential, and scientific mysteries. To explore and operate in this environment, humanity relies on two classes of advanced underwater systems: Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) and Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs).…
-

Nanotechnology at Scale: Global Market Outlook and Strategic Opportunities (2025–2032)
Look closely—closer than the eye can see. In the realm of the nanoscale, where matter is measured in billionths of a meter, a silent revolution is underway. Here, scientists are engineering materials atom-by-atom, unlocking properties that defy conventional physics. This is the world of nanotechnology, and it’s transitioning from laboratory wonder to a foundational technology…
-

Forging Digital Shields: How Nations Are Using Cyber Ranges to Prepare for Modern Conflict
In today’s interconnected world, the battlefield has extended far beyond land, sea, air, and space—it now includes the invisible yet critical domain of cyberspace. Power grids can be disrupted from a distant server, financial networks can be infiltrated without warning, and military command systems can be compromised in mere seconds. The modern era of digital…
-

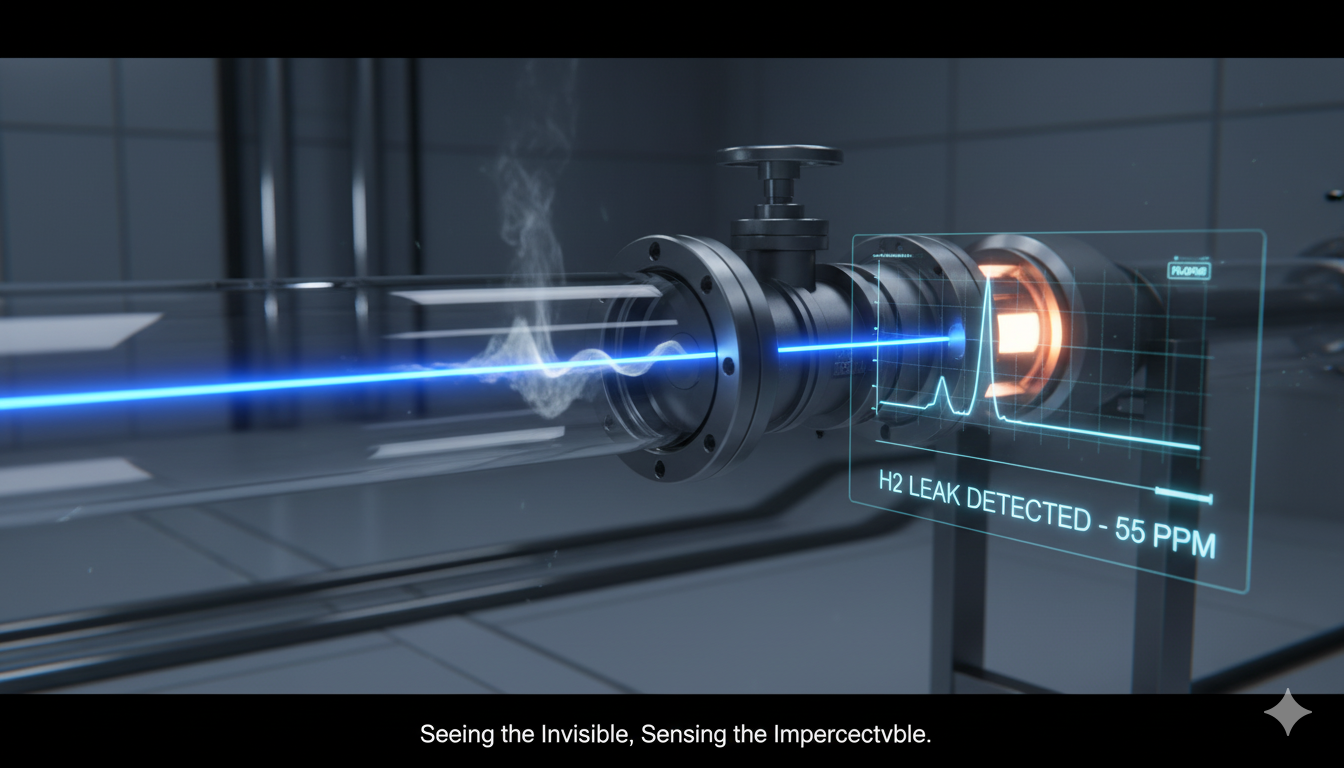
The Invisible Made Visible: A Look at Trace-Gas Sensing and the Hunt for Hydrogen
Introduction Breathing in the air around us, we seldom consider the invisible world of molecules drifting unseen—some harmless, others hazardous. Detecting trace gases at minuscule concentrations is not just a scientific pursuit; it is a necessity for ensuring safety, protecting the environment, maintaining industrial efficiency, and enabling the transition to clean energy. Whether it’s…
-

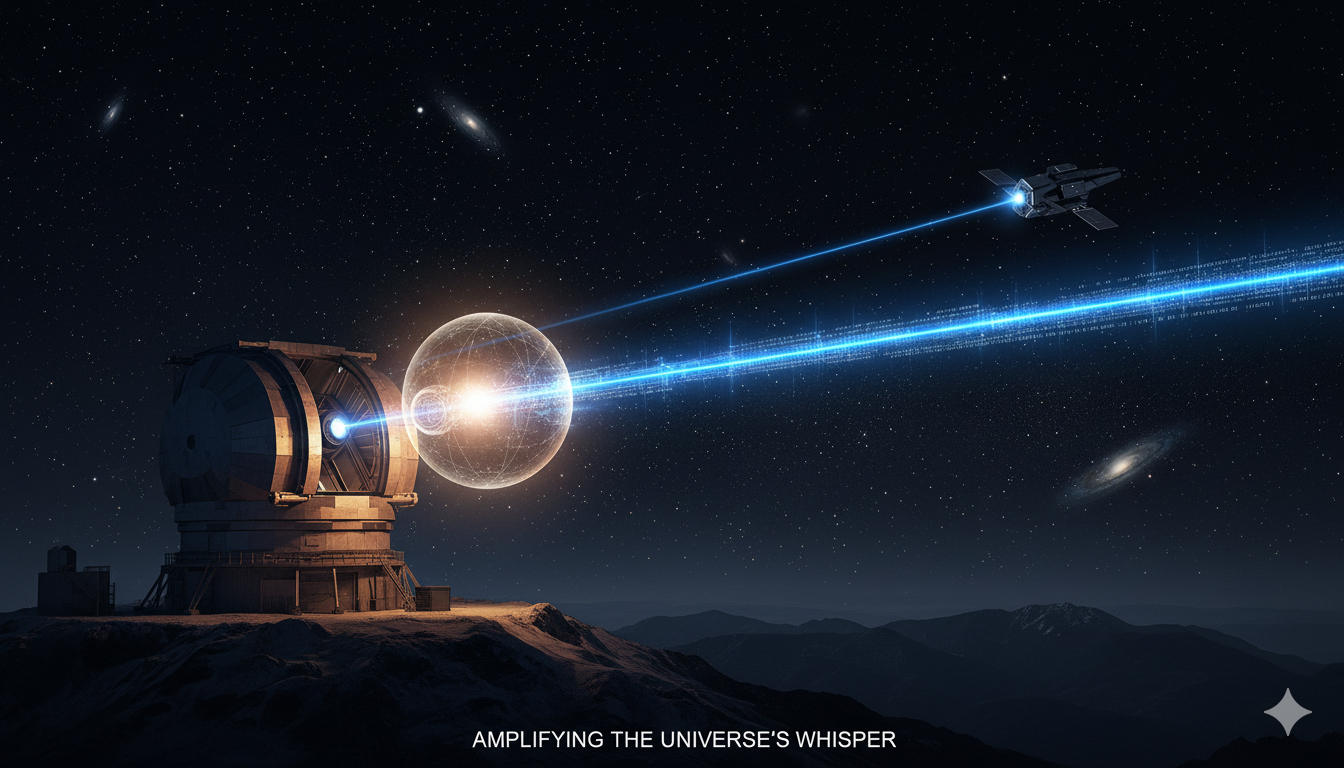
The Silent Amplifier: A Quantum Leap for Bringing Data Back From Deep Space
Imagine receiving a high-definition video, sent in real-time from a rover on Mars or a probe orbiting Jupiter. For decades, space communication has relied on radio waves—a trusted but limited technology, offering data rates more akin to a dial-up modem than modern fiber optics. The future, however, lies in light. Optical communication, using lasers…
-

The U.S. Army’s New Cybersecurity Arsenal: How Software Bills of Materials Are Fortifying National Security
In today’s digital battlefield, lines of code are becoming as critical as frontline troops. Recognizing this, the U.S. Army is deploying a powerful new tool against cyber threats: the Software Bill of Materials (SBOM). With cyber incidents in the Department of Defense continuing to rise and software supply chain attacks projected to multiply in…
STRATEGIC SUB-MAGAZINES
Modern military power emerges from the interaction of platforms, people, doctrine, and integration across domains. The Defense & Military Systems magazine is structured into focused sub-magazines that examine how combat capability is built, sustained, and employed across air, land, sea, weapons, and human systems.
Cyber & Information Warfare
Industrial outcomes are shaped as much by incentives, policy, and market structure as by engineering. Price signals, investment cycles, and regulatory frameworks quietly determine which technologies scale, stagnate, or fail.
This sub-magazine examines how markets behave under strategic pressure—where capital flows, how demand signals distort decisions, and why some industries adapt faster than others.
Explore the Cyber & Information Warfare Sub-Magazine →
Security & Threat Management
Modern security is defined by persistence, coordination, and anticipation. This sub-magazine focuses on how threats are identified, mitigated, and managed across institutions, infrastructures, and societies.
Explore the Security & Threat Management Sub-Magazine →