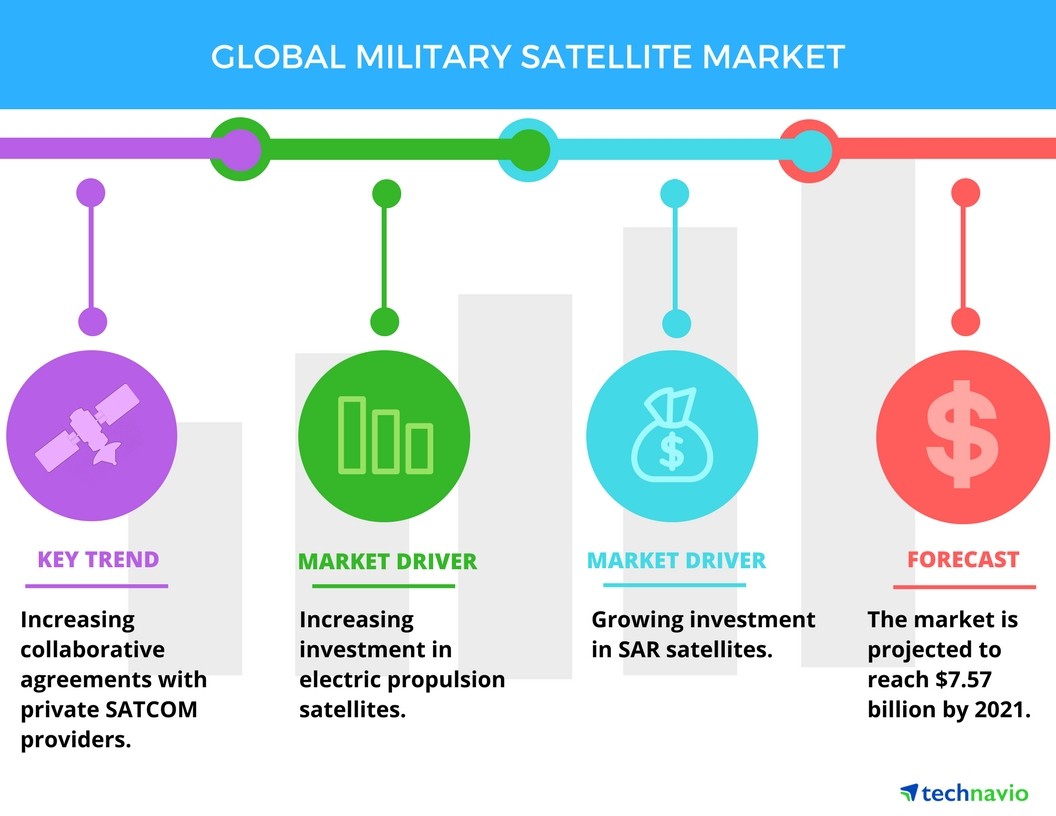
In the vast expanse of space, where technology meets strategy, military satellites emerge as critical assets, empowering nations with unparalleled surveillance, communication, and reconnaissance capabilities. As we peer into the depths of this industry, let’s uncover the market dynamics and technological trends shaping the future of military satellites. A communications satellite serves as an artificial…