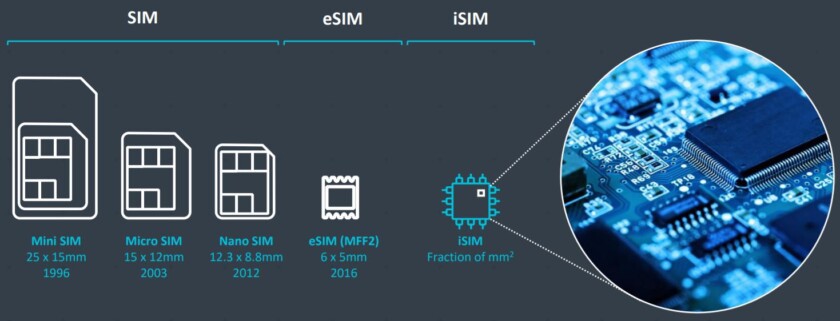
Strong IoT device authentication is required to ensure connected devices on the IoT can be trusted to be what they purport to be. Consequently, each IoT device needs a unique identity that can be authenticated when the device attempts to connect to a gateway or central server. With this unique ID in place, IT system…