A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunications signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Satellite communications networks consist of user terminals, satellites and a ground network that provides control and interface functions.
Military satellites are a measure of the nation’s military strength, operability, and the ability to attack or defend itself. These satellites give the military real-time data of movement of troops and arsenal in the enemy borders. They also facilitate high-bandwidth communication over secure channels, track and target enemy encroachment or intruding vehicles, and other military functions. Military space capability comprises Satellites for excellent imagery intelligence (photo and synthetic aperture radar), signals intelligence (COMINT, ELINT) satellite constellations, early warning for Ballistic Missile Defence, data relay satellites, Microsatellites constellations. Launch on demand.

Globally, there are between 2,500 and 2,800 active satellites, including those used for non-military purposes, such as Earth observation, or massive satellite internet constellations, like SpaceX’s Starlink. Military satellites account for about a fifth of all satellites. China has sent more satellites into space in 2020 than US and Russia. It launched 29 probes in the first nine months, while American tally was 27 and Russia launched eight, according to Bryce Space and Technology Beijing has been pushing ahead with ambitious space programme, but observers say there is still a wide gap between Chinese and US technologies. State-owned China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation was the most active individual company, with 25 launches, ahead of Elon Musk’s Space X, which had 15 launches in the period, the report said. Beijing has been pushing ahead with an ambitious space programme which includes plans to set up a space station by 2022 and a lunar station by 2045. In June, the final satellite in the BeiDou navigation system was sent into orbit, completing a network that is China’s answer to the US-owned Global Positioning System.
Currently, only six countries have the technology and finance to design, develop, and place a satellite into orbit, and even fewer countries have the capability to place multiple satellites in orbit in a single flight. Japan, Korea, and Brazil have been trying to get in league with space deployment capability, but have faced failures. Notable countries with the capability to place satellites into orbits are the US, Russia, France, Italy, China, and India. Russia, France, Italy, UK, and other nations in the European region have formed their own joint association to design, build, and launch satellites into space.
The Indian Space program under ISRO/Antrix is run and maintained by the government, and has witnessed a many successful missions than any other group of nations with similar or better technology and limited funds. In 2016, India launched 22 satellites into orbit in a single mission. Of the 22 satellites, 14 belong to foreign nations including, the US, Canada, Germany, and Indonesia. India’s successful launch of its first reusable space launch vehicle in the same period is likely to shift the military satellites market in favor of India, especially since the total budget of this project was US$ 1 billion.
Both the commercial and military satellite communication industry is evolving, as evidenced by numerous trends that one can expect to see on the horizon over the coming 18 months and beyond. The increase in small satellites, the use of low-Earth orbit (LEO), launches on reusable rocket launch vehicles and new use cases for 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) are some of the most important developments to watch.
Satellite Technology
A satellite will use an array of transponders to translate the uplink signal from the ground to a lower frequency for the downlink transmission back to the ground terminals. This frequency shifting technique reduces interference and feedback and the resulting architecture, is known as“bent pipe” architecture, that also helps reduce the cost and complexity of the satellite. Typically, the terminals, gateways and network operations center must be within the coverage of the same beam.
To meet ongoing requirements for global coverage coupled with a move towards higher bandwidth requirements has resulted in networks being operated at higher frequency underpinned by satellites that feature greater onboard functionality. Such satellites feature sophisticated on-board processors (OBP), switch matrix and phased array technology to place the routing intelligence in the satellite. This allows the ground terminals to communicate directly with one another rather than every transmission going through the network operations center.
ISR Satellites
The military and defense segments are increasingly deploying ISR satellites for strengthening the early warning capabilities of commandants, greater reconnaissance, and threat detection capabilities. The demand for this segment is influenced by factors such as the advancements in sensor technologies, predominantly in electro-optical and infrared (EO/IR) systems, and other sensor payloads.

The synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellites combine circulated radar signals and complex digital processing for creating high-resolution images of landscapes or terrains and have the ability to operate in all weather conditions. SAR satellites in the defense applications are primarily used for mapping out the terrain, locating enemy vehicles, and spotting both friendly and hostile forces. Several defense agencies are making large investments for the effective acquisition of intelligence imagery for evolving security concerns.
Military Satellite Communications
Military communications networks provide for the exchange of voice, video and data between geographically dispersed elements of a battle force. Trends driving spending on the military communications sector will be underpinned by software defined radio, satellite connectivity and network-centric IP-based communications. Satellite communications networks consist of user terminals, satellites and a ground network that provides control and interface functions. The benefit of a satellite communications network lies in its ability to link users to voice, video and data information where other forms of terrestrial networks may not be feasible. The advantages and disadvantages of this form of communication are highly dependent on the satellite and network configuration.
Communication segment of the market is expected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period. This is due to the development of advanced communication systems on the battlefield. The development of tactical communication systems, tactical data links, modern network-centric battle force capabilities, and advanced SATCOMs are some of the significant applications of military communication satellites.
Military satellite communications have typically focused on C-band and X-band operations, but as use of satellite terminals has increased, so these bands have become increasingly capacity constrained and increasingly expensive. Bandwidth demand over the years has increased driven in part by continued growth in intelligence requirements and the expansion of UAS platform usage to incorporate BLOS (beyond line of sight) operations. This has led to the use of systems operating at higher frequencies such as Ku-band and Ka-band.
C4ISR
Militaries, across the globe, are strengthening C4ISR systems that essentially need strong and secure communication channels accessible from anywhere by the defense forces. The C4ISR systems market is slated to grow in response to the increasing demand for better security, control, and co-ordination. This will increase the demand in favor of military communication and ISR satellites, during the forecast period.
Improved use of SATCOM will simplify the integration of C4ISR, enable better use of UAVs and more advanced administrative, support, and personal welfare services. The SATCOMs are also expected to extend to new terrestrial communications networks that will improve the operational agility and border protection. To overcome the challenges posed by command, control, communications, computers, intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (C4ISR), advanced Ka-band, SATCOM solutions are developed. These trends will support the continued use of military satellite communications (milsatcoms) as key enablers in completing the C4ISR jigsaw and acting as critical nodes in the net-centric communications environment. This is reflected by the broad range of terminal solutions available, targeting requirements across the land, air and naval domains.
Small Sats
Both the commercial and military satellite communication industry is evolving, as evidenced by numerous trends that one can expect to see on the horizon over the coming 18 months and beyond. The increase in small satellites, the use of high-throughput satellites and low-Earth orbiting (LEO) satellites, launches on reusable rocket launch vehicles, satellites with all-electric propulsion and new use cases for 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT) are some of the are among the game-changing innovations enabling a range of solutions from digital financial services to better health care to smarter cities.
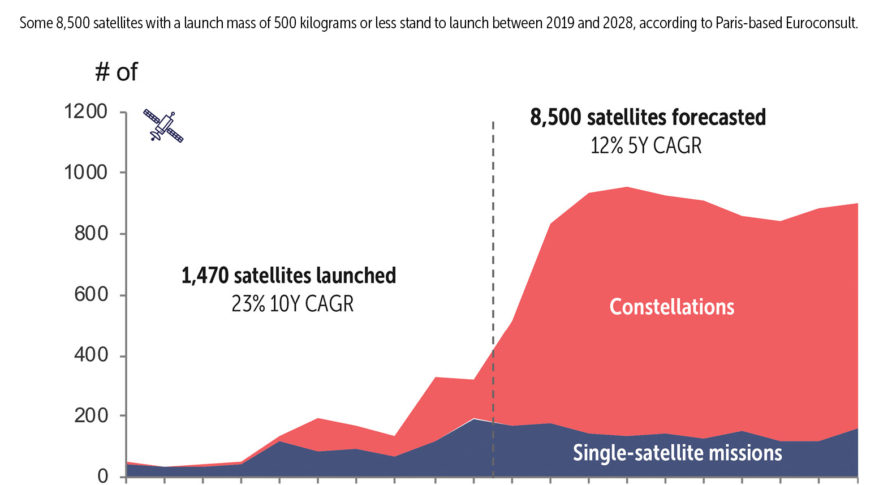
The micro, nano, and pico-sized satellites are mass produced satellite systems available in market, and are currently in service. Since the introduction of nano satellites in 2013, 94 nano satellites were launched into orbit within a year. Following this, the launch cost per nano satellites went up due to the demand. It is expected that, by the end of 2020, there will be over 1000 nano satellites orbiting earth.
The miniaturization of sensory payloads is identified as one of the key trends behind the growth of the military satellite market. Technological advancements have enabled the miniaturization of the satellites and this helps in the reduction of the overall weight and in optimizing the performance. The miniaturized radar camera is cost-effective and industry viable due to consumption of less power. The miniaturized radar camera produces better quality images than the traditional designs. Such benefits will induce defense agencies to adopt miniaturized sensors and computers to reduce cost overruns.
Mobile Satellite communications;
Despite the proliferation in cellular and terrestrial personal communication services around the world, there will still be vast geographic areas not covered by any wireless terrestrial communications. These areas are open fields for mobile and personal satellite communications, and they are key markets for the operators of geostationary satellites, such as INMARSAT, and of non-geostationary satellite constellations, such as IRIDIUM and GLOBALSTAR.
Furthermore, the growing demand for unmanned aerial vehicles has resulted into the need for constant guidance and navigation in order to avoid mid air collision. The military satellites are an effective medium for guiding the UAVs. Moreover, these satellites are able to cover a larger area and can even provide communication to remote locations.

Furthermore, the military satellites have highly flexible networking and can be used from moving platforms such as aircrafts, vehicles and ships. In addition, the growing concern for terrorism globally has driven the need for tactical communication systems to be deployed by most of the military forces across the world. The tactical communication systems help in providing secured communication platform between the military troops. Military satellites are an integral part of any tactical communication systems. Thus, the growing demand for these communication systems is further driving the demand for military satellites largely.
Furthermore, antenna gain is proportional to area and frequency, so higher operating frequencies translate to smaller antennas for the same gain enabling smaller satellite terminal equipment and pushing the concept of COTM/SOTM (communications on the move/satellite on the move) into the hands of individual soldiers. The narrower beam width of a higher frequency signal allows for more and narrower spot-beam operation which can be further enabled through the use of phased arrays.
However, there are certain restraints which are hindering the growth of the market. There is time gap while communicating through satellites which can be very risky during combats. Furthermore the satellite needs to stay in its own orbit in order to function properly. In addition, a satellite cannot be repaired once it is launched. Another major factor is the high cost of military satellites which might not be feasible for underdeveloped nations. The above mentioned issues are some of the key reasons pulling down the growth of the market. Nevertheless the ongoing research and development in defense sector is expected to lower the prices of the satellites in the near future. In addition, the repair of satellites is expected to be possible in future with the help of manned space ships.
Global Market
Global Commercial & Military Satellite Market is Expected to Grow at a CAGR of 76.6% with a Cumulative $195.11 Billion Over the Period 2020-2028, according to ResearchAndMarkets.com
The US is likely lead the global military satellites market, followed by China, UK, India, Russia, Germany, and France. Countries like Pakistan, Egypt, Nigeria, Algeria, Ukraine, South Africa, Brazil, Japan, Canada, Indonesia, Singapore, and few Arabian Countries will be the prospective markets for military satellites in the forecast period 2018-2023.
By geography, the market can be bifurcated into five strategic regions which include North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East and Africa and Latin America among others. North America is expected to have the largest market for military satellites. The presence of developed countries such as the U.S. and Canada is primarily driving the demand for military satellites in this region. Moreover, these countries focus on maintaining their defense abilities. Europe is expected to grow significantly owning to the presence of countries such as Germany, France and the U.K. which focus on investing heavily towards keeping their defense sector updated with the latest weapons and equipments. However, Asia Pacific has been identified to be the most attractive region during the forecast period.
The Americas will be the major contributor to the military satellite market and is the largest operator of remotely piloted aircraft that necessitates the integration of a satellite-based support mechanisms to cater to the growing demand for surveillance and security-related applications. The changing nature of battlefield and the development of a secure tactical waveform that can work on both commercial and government satellites will contribute to the growth of the military satellite market.
Asia Pacific region is anticipated to have the highest growth during the forecast period, owing to growth in military satellite development in this region by countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea among others. Japan has launched its first military satellite in Jan 2017 and by the end of the Jun 2018, the country has launched 8 intelligence-gathering satellites into the orbit. South Korea is also currently developing a constellation of five high-power military surveillance satellites under the project called “Project 425”. Republic of Korea’s (ROK’s) Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA) has invested about USD 900 million for this project and has selected Korean Aerospace Industries, Hanwha Systems and Thales Alenia Space for this project. Project 425 is expected to be deployed in 2023. Other than these countries, China and are also investing in satellite technology improving their communication capacity.
Key Vendors
The vendors in the military satellite must offer cost-effective and high-quality satellite systems equipped with the latest technologies. In addition to market conditions, government support, and industry development, factors such as in-house manufacturing capabilities, product offerings, R&D investments, newer technologies, global footprint network, and a strong client base also play a significant role in the performance of the vendors.

Key Manufacturers Like The Boeing Company, Thales Alenia Space, Airbus SE, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Raytheon Company, Indian Space Research Organisation, ISS, Reshetnev, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, OHB SE,
Elbit System Ltd, Viasat, Inc..
References and Resources also include:
 International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
International Defense Security & Technology Your trusted Source for News, Research and Analysis
